Page 113 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 113
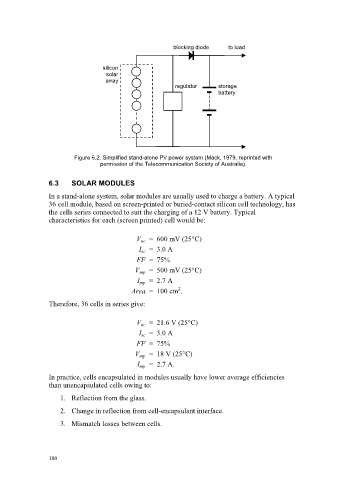
blocking diode to load
silicon
solar
array
regulator storage
battery
Figure 6.2. Simplified stand-alone PV power system (Mack, 1979, reprinted with
permission of the Telecommunication Society of Australia).
6.3 SOLAR MODULES
In a stand-alone system, solar modules are usually used to charge a battery. A typical
36 cell module, based on screen-printed or buried-contact silicon cell technology, has
the cells series connected to suit the charging of a 12 V battery. Typical
characteristics for each (screen printed) cell would be:
V oc = 600 mV (25°C)
I sc = 3.0 A
FF = 75%
V mp = 500 mV (25°C)
I mp = 2.7 A
2
Area = 100 cm .
Therefore, 36 cells in series give:
V oc = 21.6 V (25°C)
I sc = 3.0 A
FF = 75%
V mp = 18 V (25°C)
I mp = 2.7 A.
In practice, cells encapsulated in modules usually have lower average efficiencies
than unencapsulated cells owing to:
1. Reflection from the glass.
2. Change in reflection from cell-encapsulant interface.
3. Mismatch losses between cells.
100