Page 156 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 156
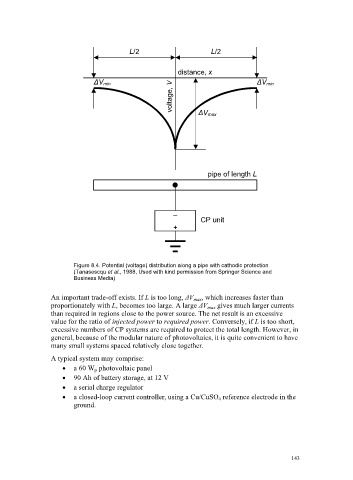
L/2 L/2
distance, x
voltage, V
ǻV min ǻV min
ǻV max
pipe of length L
–
CP unit
+
Figure 8.4. Potential (voltage) distribution along a pipe with cathodic protection
(Tanasescqu et al., 1988, Used with kind permission from Springer Science and
Business Media)
An important trade-off exists. If L is too long, ǻV max , which increases faster than
proportionately with L, becomes too large. A large ǻV max gives much larger currents
than required in regions close to the power source. The net result is an excessive
value for the ratio of injected power to required power. Conversely, if L is too short,
excessive numbers of CP systems are required to protect the total length. However, in
general, because of the modular nature of photovoltaics, it is quite convenient to have
many small systems spaced relatively close together.
A typical system may comprise:
x a 60 W p photovoltaic panel
x 90 Ah of battery storage, at 12 V
x a serial charge regulator
x a closed-loop current controller, using a Cu/CuSO 4 reference electrode in the
ground.
143