Page 14 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume II
P. 14
Distillation 3
’/ I .o
Mol Fraction Light Component
in Liquid Phase, x
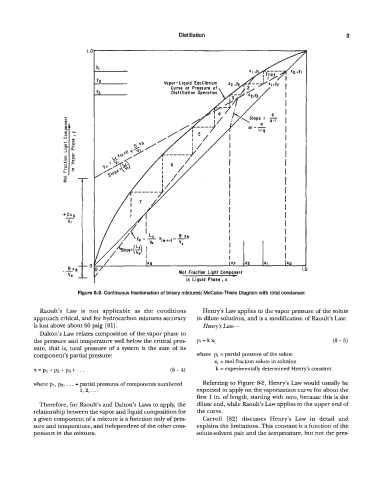
Figure 8-2. Continuous fractionation of binary mixtures; McCabe-Thiele Diagram with total condenser.
Raoult’s Law is not applicable as the conditions Henry’s Law applies to the vapor pressure of the solute
approach critical, and for hydrocarbon mixtures accuracy in dilute solutions, and is a modification of Raoult’s Law:
is lost above about 60 psig [81]. Henry’s Law
Dalton’s Law relates composition of the vapor phase to
the pressure and temperature well below the critical pres-
sure, that is, total pressure of a system is the sum of its
component’s partial pressure: where pi = partial pressure of the solute
xi = mol fraction solute in solution
lc=pp1+ p2 + p3 + . . . (8 - 4) k = experimentally determined Henry’s constant
where p1, p2, . . . = partial pressures of components numbered Referring to Figure 8-2, Henry’s Law would usually be
1, 2,. . . expected to apply on the vaporization curve for about the
first 1 in. of length, starting with zero, because this is the
Therefore, for Raoult’s and Dalton’s Laws to apply, the dilute end, while Raoult’s Law applies to the upper end of
relationship between the vapor and liquid composition for the curve.
a given component of a mixture is a function only of pres- Carroll [82] discusses Henry’s Law in detail and
sure and temperature, and independent of the other com- explains the limitations. This constant is a function of the
ponents in the mixture. solute-solvent pair and the temperature, but not the pres-