Page 134 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 134
3. Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) as Brain-Inspired ANN 123
The deSNN training algorithm.
1: Set deSNN parameters (including: Mod, C, Sim, and the SDSP parameters)
2: FOR every input spatio-temporal spiking pattern Pi DO
2a. Create a new output neuron i for this pattern and calculate the initial values of connection weights wi(0)
using the RO learning rule.
2b. Adjust the connection weights wi for consecutive spikes on the corresponding synapses using the STDP
learning rule.
2c. Calculate PSPimax using formula.
2d. Calculate the spiking threshold of the ith neuron.
2e. (Optional) IF the new neuron weight vector wi is similar in its initial wi(0) an final wi(T ) values after
training to the weight vector of an already trained output neuron using Euclidean distance and a similarity
threshold Sim, then merge the two neurons (as a partial case only initial or final values of the connection
weights can be considered or a weighted sum of them)
ELSE
Add the new neuron to the output neurons repository.
END IF
END FOR (Repeat for all input spatio-temporal patterns for learning)
FIGURE 6.8
The deSNN training algorithm [99].
(A) v
L2 i
L2 j
C i C j
(B) Ci Cj
w
L1
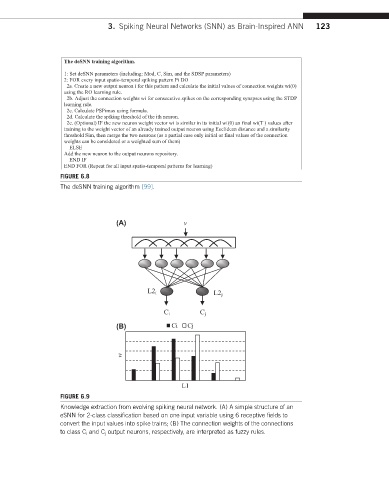
FIGURE 6.9
Knowledge extraction from evolving spiking neural network. (A) A simple structure of an
eSNN for 2-class classification based on one input variable using 6 receptive fields to
convert the input values into spike trains; (B) The connection weights of the connections
to class C i and C j output neurons, respectively, are interpreted as fuzzy rules.