Page 129 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 129
118 CHAPTER 6 Evolving and Spiking Connectionist Systems
3. “Open” evolving structure, where new input variables (relevant to the task), new
outputs (e.g., classes), new connections, and neurons are added/evolved “on the
fly”;
4. Both data learning and knowledge representation is facilitated in a comprehen-
sive and flexible way, for example, supervised learning, unsupervised learning,
evolving clustering, “sleep” learning, forgetting/pruning, fuzzy rule insertion,
and extraction;
5. Active interaction with other ECOSs and with the environment in a multimodal
fashion;
6. Representing both space and time in their different scales, for example, clusters
of data, short- and long-term memory, age of data, forgetting, etc.;
7. System’s self-evaluation in terms of behavior, global error and success, and
related knowledge representation.
2.2 ECOS REALIZATIONS AND AI APPLICATIONS
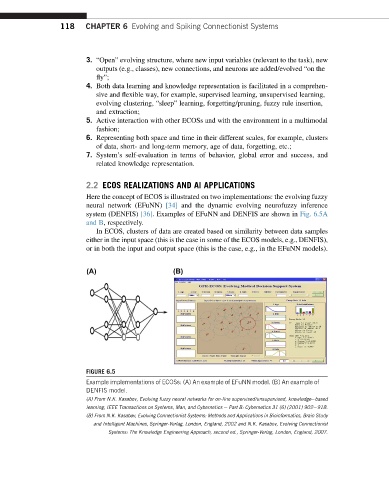
Here the concept of ECOS is illustrated on two implementations: the evolving fuzzy
neural network (EFuNN) [34] and the dynamic evolving neurofuzzy inference
system (DENFIS) [36]. Examples of EFuNN and DENFIS are shown in Fig. 6.5A
and B, respectively.
In ECOS, clusters of data are created based on similarity between data samples
either in the input space (this is the case in some of the ECOS models, e.g., DENFIS),
or in both the input and output space (this is the case, e.g., in the EFuNN models).
FIGURE 6.5
Example implementations of ECOSs: (A) An example of EFuNN model. (B) An example of
DENFIS model.
(A) From N.K. Kasabov, Evolving fuzzy neural networks for on-line supervised/unsupervised, knowledgeebased
learning, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics e Part B: Cybernetics 31 (6) (2001) 902e918.
(B) From N.K. Kasabov, Evolving Connectionist Systems: Methods and Applications in Bioinformatics, Brain Study
and Intelligent Machines, Springer-Verlag, London, England, 2002 and N.K. Kasabov, Evolving Connectionist
Systems: The Knowledge Engineering Approach, second ed., Springer-Verlag, London, England, 2007.