Page 125 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 125
114 CHAPTER 6 Evolving and Spiking Connectionist Systems
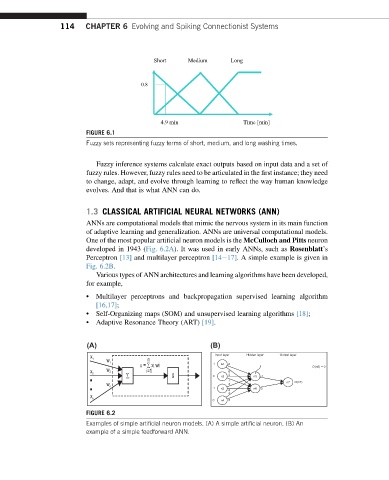
Short Medium Long
0.8
4.9 min Time [min]
FIGURE 6.1
Fuzzy sets representing fuzzy terms of short, medium, and long washing times.
Fuzzy inference systems calculate exact outputs based on input data and a set of
fuzzy rules. However, fuzzy rules need to be articulated in the first instance; they need
to change, adapt, and evolve through learning to reflect the way human knowledge
evolves. And that is what ANN can do.
1.3 CLASSICAL ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS (ANN)
ANNs are computational models that mimic the nervous system in its main function
of adaptive learning and generalization. ANNs are universal computational models.
One of the most popular artificial neuron models is the McCulloch and Pitts neuron
developed in 1943 (Fig. 6.2A). It was used in early ANNs, such as Rosenblatt’s
Perceptron [13] and multilayer perceptron [14e17]. A simple example is given in
Fig. 6.2B.
Various types of ANN architectures and learning algorithms have been developed,
for example,
• Multilayer perceptrons and backpropagation supervised learning algorithm
[16,17];
• Self-Organizing maps (SOM) and unsupervised learning algorithms [18];
• Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) [19].
(A) (B)
FIGURE 6.2
Examples of simple artificial neuron models. (A) A simple artificial neuron. (B) An
example of a simple feedforward ANN.