Page 268 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 268
260 CHAPTER 12 Computational Intelligence in the Time
We discovered that a darknet traffic pattern can be successfully described by the
following 17 features related to the statistics of darknet packets [22]:
(1) #Total Packets (2, 3) Avg and Std of Time Spans of
Packets
(4) #Source Ports (5, 6) Avg and Std of #Packets from
Source Ports
(7) #Destination IPs (8, 9) Avg and Std of #Packets from
Dest. IPs
(10) #Destination Ports (11, 12) Avg and Std of #Packets
from Dest. Ports
(13) #Protocol Types (14, 15) Avg and Std of Payload
Sizes
(16, 17) Avg and Std of
Spans of Dest. IP
Numbers.
Once a darknet traffic pattern for a specific source host is transformed into the
17-dimensional feature vector, machine learning techniques can be applied to cluster
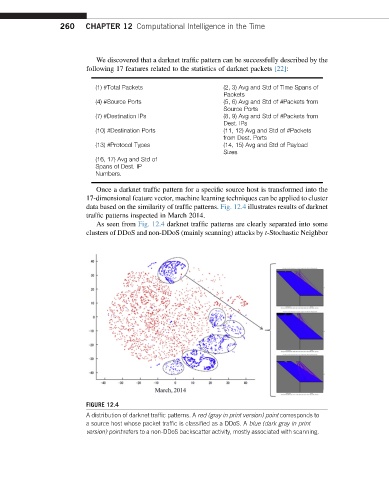
data based on the similarity of traffic patterns. Fig. 12.4 illustrates results of darknet
traffic patterns inspected in March 2014.
As seen from Fig. 12.4 darknet traffic patterns are clearly separated into some
clusters of DDoS and non-DDoS (mainly scanning) attacks by t-Stochastic Neighbor
FIGURE 12.4
A distribution of darknet traffic patterns. A red (gray in print version) point corresponds to
a source host whose packet traffic is classified as a DDoS. A blue (dark gray in print
version) point refers to a non-DDoS backscatter activity, mostly associated with scanning.