Page 281 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 281
274 CHAPTER 13 Multiview Learning in Biomedical Applications
1
applied voxel-wise generalized linear models are based on unrealistic assumptions
(e.g., statistically independence of variables) that do not reflect the underlying
neurological principles thus hampering the interpretation of the results. In the
past decade, the introduction of more sophisticated methods based on machine
learning in the field of neuroscience has paved the way for the development of a
framework for the automated decoding of variables of interest from MRI data.
These methods have the potential to give significant insights about the causes of
the phenomena under study and have already been successfully applied in practical
applications such as single-subject classification. However, machine learning
models have to take up to the challenges that are intrinsic to the analysis of neuro-
imaging data that are the extreme high dimensionality of the observations, the
high redundancy present in the data, and the relatively small number of available
samples. For this reason existing methods need to be tailored to these applications.
In addition, the recent advances in MRI technologies have made available a wide
range or modalities (or views) describing several aspects of human brain, such
as the representation of functional behavior through functional MRI, and the
reconstruction of bundles of synaptic fascicles through diffusion tensor imaging.
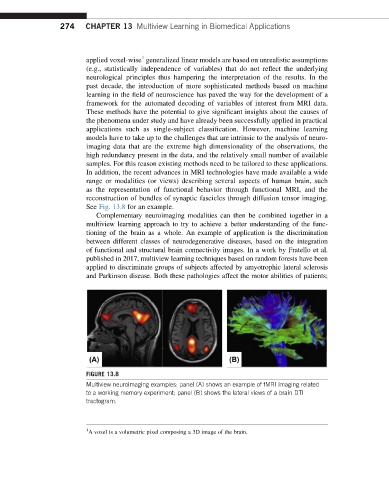
See Fig. 13.8 for an example.
Complementary neuroimaging modalities can then be combined together in a
multiview learning approach to try to achieve a better understanding of the func-
tioning of the brain as a whole. An example of application is the discrimination
between different classes of neurodegenerative diseases, based on the integration
of functional and structural brain connectivity images. In a work by Fratello et al.
published in 2017, multiview learning techniques based on random forests have been
applied to discriminate groups of subjects affected by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
and Parkinson disease. Both these pathologies affect the motor abilities of patients;
FIGURE 13.8
Multiview neuroimaging examples: panel (A) shows an example of fMRI imaging related
to a working memory experiment; panel (B) shows the lateral views of a brain DTI
tractogram.
1
A voxel is a volumetric pixel composing a 3D image of the brain.