Page 51 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 51
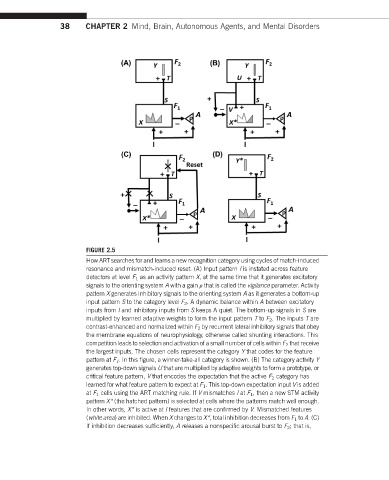
38 CHAPTER 2 Mind, Brain, Autonomous Agents, and Mental Disorders
FIGURE 2.5
How ARTsearches for and learns a new recognition category using cycles of match-induced
resonance and mismatch-induced reset. (A) Input pattern I is instated across feature
detectors at level F 1 as an activity pattern X, at the same time that it generates excitatory
signals to the orienting system A withagain r that is called the vigilance parameter. Activity
pattern X generates inhibitory signals to the orienting system A as it generates a bottom-up
input pattern S to the category level F 2 . A dynamic balance within A between excitatory
inputs from I and inhibitory inputs from S keeps A quiet. The bottom-up signals in S are
multiplied by learned adaptive weights to form the input pattern T to F 2 . The inputs T are
contrast-enhanced and normalized within F 2 by recurrent lateral inhibitory signals that obey
the membrane equations of neurophysiology, otherwise called shunting interactions. This
competition leads to selection and activation of a small number of cells within F 2 that receive
the largest inputs. The chosen cells represent the category Y that codes for the feature
pattern at F 1 . In this figure, a winner-take-all category is shown. (B) The category activity Y
generates top-down signals U that are multiplied by adaptive weights to form a prototype, or
critical feature pattern, V that encodes the expectation that the active F 2 category has
learned for what feature pattern to expect at F 1 . This top-down expectation input V is added
at F 1 cells using the ART matching rule. If V mismatches I at F 1 , then a new STM activity
pattern X* (the hatched pattern) is selected at cells where the patterns match well enough.
In other words, X* is active at I features that are confirmed by V. Mismatched features
(white area) are inhibited. When X changes to X*, total inhibition decreases from F 1 to A.(C)
If inhibition decreases sufficiently, Areleases a nonspecific arousal burst to F 2 ;that is,