Page 189 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 189
Hybrid vehicle design CHAPTER 7.1
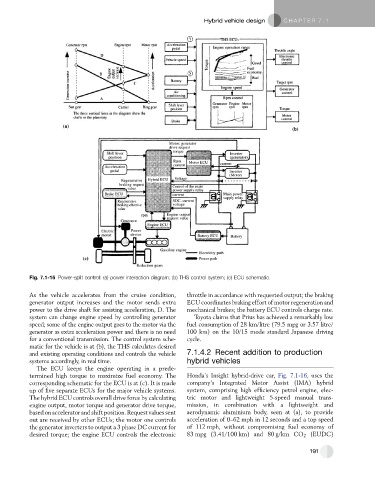
Fig. 7.1-15 Power-split control: (a) power interaction diagram; (b) THS control system; (c) ECU schematic.
As the vehicle accelerates from the cruise condition, throttle in accordance with requested output; the braking
generator output increases and the motor sends extra ECU coordinates braking effort of motor regeneration and
power to the drive shaft for assisting acceleration, D. The mechanical brakes; the battery ECU controls charge rate.
system can change engine speed by controlling generator Toyota claims that Prius has achieved a remarkably low
speed; some of the engine output goes to the motor via the fuel consumption of 28 km/litre (79.5 mpg or 3.57 litre/
generator as extra acceleration power and there is no need 100 km) on the 10/15 mode standard Japanese driving
for a conventional transmission.The controlsystemsche- cycle.
matic for the vehicle is at (b), the THS calculates desired
and existing operating conditions and controls the vehicle 7.1.4.2 Recent addition to production
systems accordingly, in real time. hybrid vehicles
The ECU keeps the engine operating in a prede-
termined high torque to maximize fuel economy. The Honda’s Insight hybrid-drive car, Fig. 7.1-16, uses the
corresponding schematic for the ECU is at (c). It is made company’s Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) hybrid
up of five separate ECUs for the major vehicle systems. system, comprising high efficiency petrol engine, elec-
The hybrid ECU controls overall drive force by calculating tric motor and lightweight 5-speed manual trans-
engine output, motor torque and generator drive torque, mission, in combination with a lightweight and
based onacceleratorandshiftposition.Requestvaluessent aerodynamic aluminium body, seen at (a), to provide
out are received by other ECUs; the motor one controls acceleration of 0–62 mph in 12 seconds and a top speed
the generator inverters to output a 3 phase DC current for of 112 mph, without compromising fuel economy of
desired torque; the engine ECU controls the electronic 83 mpg (3.41/100 km) and 80 g/km CO 2 (EUDC)
191