Page 198 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 198
CH AP TER 7 .1 Hybrid vehicle design
frequency equals the fundamental motor frequency. A operation. Provision is also made to inhibit hybrid oper-
large speed ratio, 1.5:1, is thus possible. ation until 30% SOC is reached so silent and zero-
emission night-time, or in-tunnel, operation is made
7.1.5.4 Advanced hybrid truck possible. In hybrid mode SOC is maintained at 65–70%,
at which point the generated power, from the generator,
Mitsubishi have been prominent in hybrid truck manu- and the regenerative power, from the motor, provide
facture and have recently developed a heavier, municipal, sufficient charging.
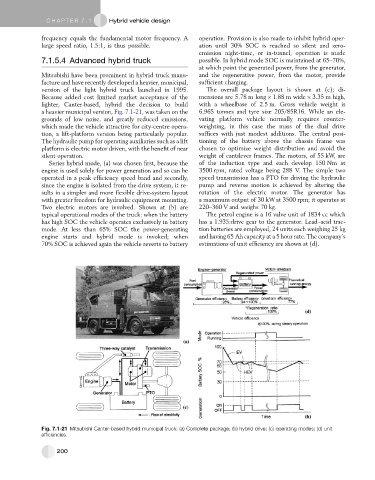
version of the light hybrid truck launched in 1995. The overall package layout is shown at (c); di-
Because added cost limited market acceptance of the mensions are 5.78 m long 1.88 m wide 3.35 m high,
lighter, Canter-based, hybrid the decision to build with a wheelbase of 2.5 m. Gross vehicle weight is
a heavier municipal version, Fig. 7.1-21, was taken on the 6.965 tonnes and tyre size 205/85R16. While an ele-
grounds of low noise, and greatly reduced emissions, vating platform vehicle normally requires counter-
which made the vehicle attractive for city-centre opera- weighting, in this case the mass of the dual drive
tion, a lift-platform version being particularly popular. suffices with just modest additions. The central posi-
The hydraulic pump for operating auxiliaries such as a lift tioning of the battery above the chassis frame was
platform is electric motor driven, with the benefit of near chosen to optimize weight distribution and avoid the
silent operation. weight of cantilever frames. The motors, of 55 kW, are
Series hybrid mode, (a) was chosen first, because the of the induction type and each develop 150 Nm at
engine is used solely for power generation and so can be 3500 rpm, rated voltage being 288 V. The simple two
operated in a peak efficiency speed band and secondly, speed transmission has a PTO for driving the hydraulic
since the engine is isolated from the drive system, it re- pump and reverse motion is achieved by altering the
sults in a simpler and more flexible drive-system layout rotation of the electric motor. The generator has
with greater freedom for hydraulic equipment mounting. a maximum output of 30 kW at 3500 rpm; it operates at
Two electric motors are involved. Shown at (b) are 220–360 V and weighs 70 kg.
typical operational modes of the truck: when the battery The petrol engine is a 16 valve unit of 1834 cc which
has high SOC the vehicle operates exclusively in battery has a 1.935:drive gear to the generator. Lead–acid trac-
mode. At less than 65% SOC the power-generating tion batteries are employed, 24 units each weighing 25 kg
engine starts and hybrid mode is invoked; when and having 65 Ah capacity at a 5 hour rate. The company’s
70% SOC is achieved again the vehicle reverts to battery estimations of unit efficiency are shown at (d).
Fig. 7.1-21 Mitsubishi Canter-based hybrid municipal truck: (a) Complete package; (b) hybrid drive; (c) operating modes; (d) unit
efficiencies.
200