Page 250 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 250
CH AP TER 8 .1 Types of suspension and drive
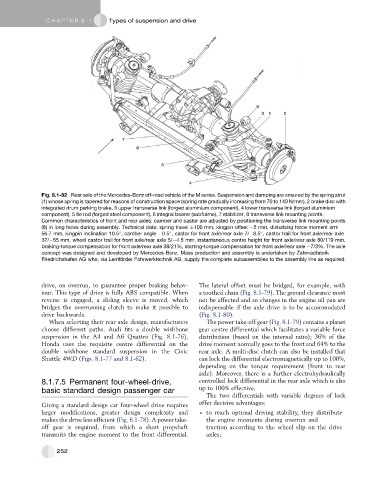
Fig. 8.1-82 Rear axle of the Mercedes-Benz off-road vehicle of the M series. Suspension and damping are ensured by the spring strut
(1) whose spring is tapered for reasons of construction space (spring rate gradually increasing from 70 to 140 N/mm), 2 brake disc with
integrated drum parking brake, 3 upper transverse link (forged aluminium component), 4 lower transverse link (forged aluminium
component), 5 tie rod (forged steel component), 6 integral bearer (subframe), 7 stabilizer, 8 transverse link mounting points.
Common characteristics of front and rear axles: camber and castor are adjusted by positioning the transverse link mounting points
(8) in long holes during assembly. Technical data: spring travel 100 mm, kingpin offset 5 mm, disturbing force moment arm
56.7 mm, kingpin inclination 10.5 , camber angle 0.5 , castor for front axle/rear axle 7/ 8.5 , castor trail for front axle/rear axle
37/ 55 mm, wheel castor trail for front axle/rear axle 5/ 4.5 mm, instantaneous centre height for front axle/rear axle 80/119 mm,
braking-torque compensation for front axle/rear axle 38/21%, starting-torque compensation for front axle/rear axle 7/3%. The axle
concept was designed and developed by Mercedes-Benz. Mass production and assembly is undertaken by Zahnradfabrik
Friedrichshafen AG who, via Lemfo ¨ rder Fahrwerktechnik AG, supply the complete subassemblies to the assembly line as required.
drive, on overrun, to guarantee proper braking behav- The lateral offset must be bridged, for example, with
iour. This type of drive is fully ABS compatible. When a toothed chain (Fig. 8.1-79). The ground clearance must
reverse is engaged, a sliding sleeve is moved, which not be affected and so changes in the engine oil pan are
bridges the overrunning clutch to make it possible to indispensable if the axle drive is to be accommodated
drive backwards. (Fig. 8.1-80).
When selecting their rear axle design, manufacturers The power take-off gear (Fig. 8.1-79) contains a planet
choose different paths. Audi fits a double wishbone gear centre differential which facilitates a variable force
suspension in the A4 and A6 Quattro (Fig. 8.1-76), distribution (based on the internal ratio); 36% of the
Honda uses the requisite centre differential on the drive moment normally goes to the front and 64% to the
double wishbone standard suspension in the Civic rear axle. A multi-disc clutch can also be installed that
Shuttle 4WD (Figs. 8.1-77 and 8.1-62). can lock the differential electromagnetically up to 100%,
depending on the torque requirement (front to rear
axle). Moreover, there is a further electrohydraulically
8.1.7.5 Permanent four-wheel-drive, controlled lock differential in the rear axle which is also
basic standard design passenger car up to 100% effective.
The two differentials with variable degrees of lock
Giving a standard design car four-wheel drive requires offer decisive advantages:
larger modifications, greater design complexity and to reach optimal driving stability, they distribute
makes the drive less efficient (Fig. 8.1-78). A power take- the engine moments during overrun and
off gear is required, from which a short propshaft traction according to the wheel slip on the drive
transmits the engine moment to the front differential. axles;
252