Page 180 - Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 180
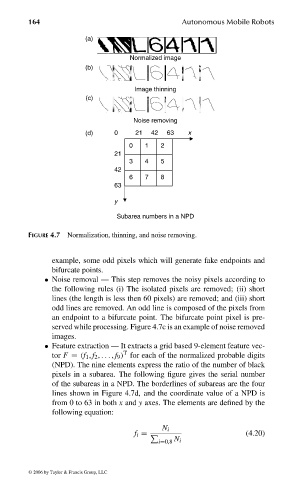
164 Autonomous Mobile Robots
(a)
Normalized image
(b)
Image thinning
(c)
Noise removing
(d) 0 21 42 63 x
0 1 2
21
3 4 5
42
6 7 8
63
y
Subarea numbers in a NPD
FIGURE 4.7 Normalization, thinning, and noise removing.
example, some odd pixels which will generate fake endpoints and
bifurcate points.
• Noise removal — This step removes the noisy pixels according to
the following rules (i) The isolated pixels are removed; (ii) short
lines (the length is less then 60 pixels) are removed; and (iii) short
odd lines are removed. An odd line is composed of the pixels from
an endpoint to a bifurcate point. The bifurcate point pixel is pre-
served while processing. Figure 4.7c is an example of noise removed
images.
• Feature extraction — It extracts a grid based 9-element feature vec-
T
tor F = (f 1 , f 2 , ... , f 9 ) for each of the normalized probable digits
(NPD). The nine elements express the ratio of the number of black
pixels in a subarea. The following figure gives the serial number
of the subareas in a NPD. The borderlines of subareas are the four
lines shown in Figure 4.7d, and the coordinate value of a NPD is
from 0 to 63 in both x and y axes. The elements are defined by the
following equation:
N i
(4.20)
f i =
i=0,8 N i
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
FRANKL: “dk6033_c004” — 2006/3/31 — 16:42 — page 164 — #16