Page 203 - Basic English Usage
P. 203
205 261
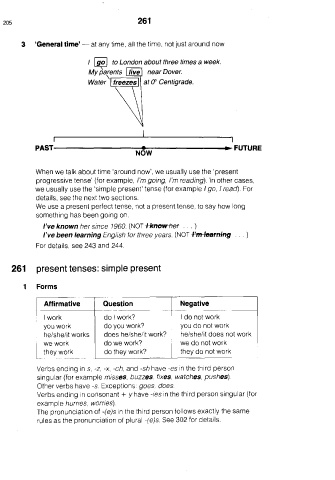
3 ‘General time’ — at any time, all the time, not just around now
1 [go] to London about three times a week.
My parents | live] near Dover.
Water at 0 Centigrade.
I |
—_6-~
—e- FUTURE
Now
P. AST
When we talk about time ‘around now’, we usually use the ‘present
progressive tense’ (for example, !’m going, I'm reading). \n other cases,
we usually use the ‘simple present’ tense (for example / go, / read). For
details, see the next two sections.
We use a present perfect tense, not a present tense, to say how long
something has been going on.
I’ve known her since 1960. (NOT #inewher ...)
I’ve been learning English for three years. (NOT Fimearning ...)
For details, see 243 and 244.
261 present tenses: simple present
1 Forms
Affirmative Question Negative
| work do } work? | do not work
you work do you work? you do not work
he/she/it works does he/she/it work? he/she/it does not work
we work do we work? we do not work
they work do they work? they do not work
Verbs ending in s, -2, -x, -ch, and -sh have -es in the third person
singular (for example misses, buzzes, fixes, watches, pushes).
Other verbs have -s. Exceptions: goes, does.
Verbs ending in consonant + y have -ies in the third person singular (for
example hurries, worries).
The pronunciation of -(e)s in the third person follows exactly the same
rules as the pronunciation of plural -(e)s. See 302 for details.