Page 41 - Basic Well Log Analysis for Geologist
P. 41
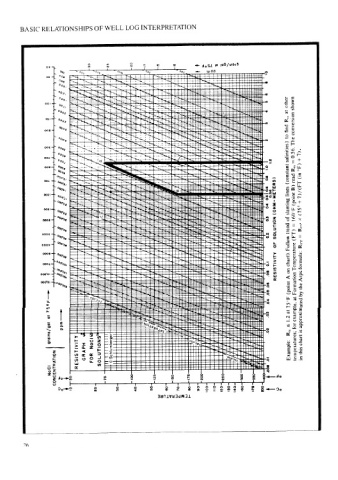
BASIC RELATIONSHIPS OF WELL LOG INTERPRETATION
30 Les +20 18 > 4oSz 10 j06/ui0s6
“Oo, Po.
Ong dd
Ca
H
20,
09,
0,
0,4, : op.
0,, Jif: other shown
09, r
at
os og, dk. R,,
ly conversion
Q0 whe find
002 4
hf
0, to
| ; YA The
S00,
00, salinities} 0.56. +7).
209, 7 =
Ys °F)
Oe R,,
06
os read
0. (constant (in
0510 lines B) 7)/(FT
%p. (OHM- METERS) (point
04 slanting +
oogi (75°
20, ; 160°F
Og, 03 of X
Wo, SOLUTION trend = R;5)
ooot —. a9. 0.2 (FT)
‘Oe =
11
coor a9: ‘Oe OF Follow Rrr
Oe, Temperature
ooo1—4 005, O. RESISTIVITY chart). formula:
My on
.08
Png. A Arps
(point the
PO, Formation
—e> at by
75°F 75°F
ot eom-~- at 1.2 example, approximated
grains/gal NoC! ts R,, for temperatures; is chart
CONCENTRATION RESISTIVITY GRAPH FOR SOLUTIONS Sch © Example: this in
NaCl a i ~<«—dJo
° ' 20 40 100 a § <— 20
oO 10 °
SunivedadW3al
26