Page 171 - Basic physical chemistry for the atmospheric sciences
P. 171
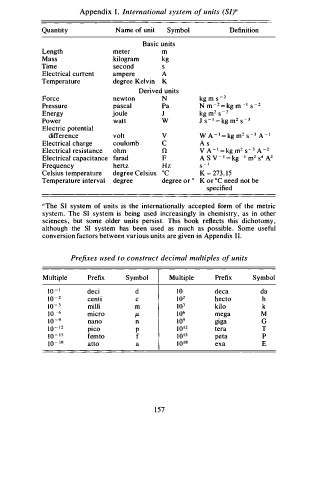
Appendix I. International system o f units (SI)"
Quantity Name of unit Symbol Definition
Basic units
Length meter m
Mass kilogram kg
Time second s
Electrical current ampere A
Temperature degree Kelvin K
Derived units
Force newton N kg m s - 2
2
s
Pressure pascal Pa N m - = kg m - 1 - 2
Energy joule J kg m s - 2
2
Power watt w j S - I = kg m2 S - 3
Electric potential
difference volt V W A - 1 = kg m2 s - 3 A - 1
Electrical charge coulomb C A s
Electrical resistance ohm n v A - I = kg m s - 3 A - 2
2
Electrical capacitance farad F A S V - 1 = k g - 1 m2 s 4 A 2
Frequency hertz Hz s - 1
Celsius temperature degree Celsius °C K - 27 . 15
3
Temperature interval degree degree or ° K or °C need not be
specified
0 T he SI system of units is the internationally accepted form of the metric
system. The SI system is being used increasingly in chemistry, as in other
sciences , but some older units persist. This book reflects this dichotomy ,
although the SI system has been used as much as possible. Some useful
conversion factors between various units are given in Appendix II.
Prefixes used to construct decimal multiples o f units
Multiple Prefix Symbol Multiple Prefix Symbol
1 0 - 1 deci d 10 deca da
1 0 - 2 centi c 1 0 2 hecto h
10 - 3 mi Iii m 1 03 kilo k
1 0 - 6 micro µ 1 0 6 mega M
1 0 - 9 nano n 1 0 9 giga G
1 0 - 1 2 pico p 1 0 1 2 tera T
10 - 1 5 fem to f 1 0 1 5 peta p
1 0 - 1 8 atto a 10 1 8 exa E
1 5 7