Page 194 - Basic physical chemistry for the atmospheric sciences
P. 194
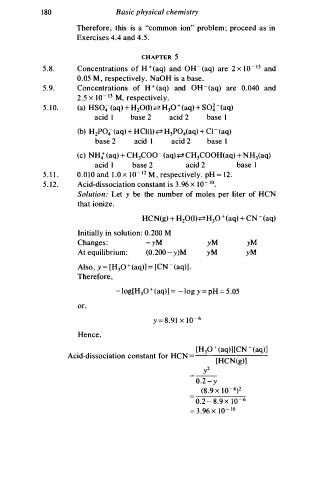
1 8 0 Basic physical chemistry
Therefore, this is a "common ion" problem ; proceed as in
4
Exercises 4.4 and . 5 .
CHAPTER 5
5 . 8 . Concentrations o f H + (aq) and OH - ( aq) are 2 x 1 0 - 1 3 and
0.05 M , respectively. NaOH is a base.
5 . 9. Concentrations of H + (aq) and oH - (aq) are 0 . 0 40 and
2 . 5 x 1 0 - 13 M, respectively.
5 . 1 0 . (a) HS04- (aq) + H 2 0(l) � H 3 0 + ( aq) + Sol - ( aq)
acid I base 2 acid 2 base 1
(b) H2P04 (aq) + HCl(l) � H 3 POiaq) + Cl - (aq)
base 2 acid I acid 2 base I
(c) NH4+ (aq) + CH COO - ( aq) � CH COOH(aq) + N H 3(aq)
3
3
acid I base 2 acid 2 base 1
5 . 1 1 . 0 . 0 1 0 and 1 . 0 x 1 0 - 12 M , respectively. pH = 1 2 .
5 . 1 2 . Acid-dissociation constant s 3 . 9 6 x 1 0 - 1 0 •
i
Solution: Let y be the number of moles per liter of HCN
that ionize.
HC N (g) + H 2 0(l)� H 30 + (aq) + CN - (aq)
0
Initially in solution: . 2 00 M
s
Change : - yM yM yM
At equilibrium: (0.2 00 - y)M yM yM
Also, y = [H3 0 + ( aq)] = [CN - ( aq)] .
Therefore,
- log[H 0 + (aq)] = - log y = pH = 5 .05
3
or,
y = 8 . 9 1 x 1 0 - 6
Hence ,
[H 3 0 + (aq)][CN - ( aq)]
Acid-dissociation constant for HCN [HCN(g)]
2
y
0. 2 - y
(8.9 x 1 0 - 6) 2
0 . 2 - 8 .9 X 1 0 - 6
= .96 x 1 0 - 1 0
3