Page 113 - Basics of MATLAB and Beyond
P. 113
matrices, strings, structures, or other cell arrays. For example, to create
a2 × 2 × 2 cell array we can type:
a = {[1 2] ’hello’; 3[5;6]};
b = {spiral(3) eye(2) ; ’good’ ’bad’};
c = cat(3,a,b);
The cat function concatenates arrays a and b along dimension number 3.
To visualize this array we can use celldisp and cellplot as we did
before. For example:
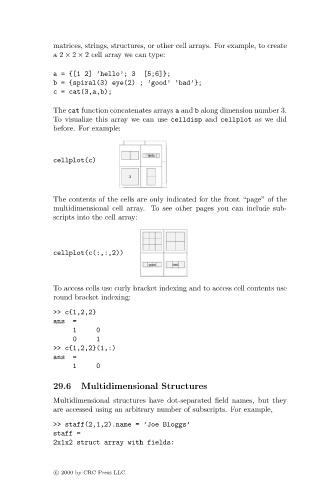
cellplot(c)
The contents of the cells are only indicated for the front “page” of the
multidimensional cell array. To see other pages you can include sub-
scripts into the cell array:
cellplot(c(:,:,2))
To access cells use curly bracket indexing and to access cell contents use
round bracket indexing:
>> c{1,2,2}
ans =
1 0
0 1
>> c{1,2,2}(1,:)
ans =
1 0
29.6 Multidimensional Structures
Multidimensional structures have dot-separated field names, but they
are accessed using an arbitrary number of subscripts. For example,
>> staff(2,1,2).name = ’Joe Bloggs’
staff =
2x1x2 struct array with fields:
c 2000 by CRC Press LLC