Page 117 - Basics of MATLAB and Beyond
P. 117
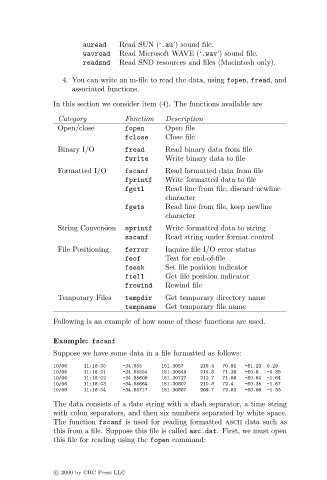
auread Read SUN (‘.au’) sound file.
wavread Read Microsoft WAVE (‘.wav’) sound file.
readsnd Read SND resources and files (Macintosh only).
4. You can write an m-file to read the data, using fopen, fread, and
associated functions.
In this section we consider item (4). The functions available are
Category Function Description
Open/close fopen Open file
fclose Close file
Binary I/O fread Read binary data from file
fwrite Write binary data to file
Formatted I/O fscanf Read formatted data from file
fprintf Write formatted data to file
fgetl Read line from file, discard newline
character
fgets Read line from file, keep newline
character
String Conversion sprintf Write formatted data to string
sscanf Read string under format control
File Positioning ferror Inquire file I/O error status
feof Test for end-of-file
fseek Set file position indicator
ftell Get file position indicator
frewind Rewind file
Temporary Files tempdir Get temporary directory name
tempname Get temporary file name
Following is an example of how some of these functions are used.
Example: fscanf
Suppose we have some data in a file formatted as follows:
10/06 11:18:00 -34.855 151.3057 216.4 70.91 -61.23 0.29
10/06 11:18:01 -34.85554 151.30649 214.8 71.38 -60.8 -0.88
10/06 11:18:02 -34.85609 151.30727 212.7 71.86 -60.64 -1.64
10/06 11:18:03 -34.85664 151.30807 210.8 72.4 -60.35 -1.67
10/06 11:18:04 -34.85717 151.30887 209.7 72.83 -60.06 -1.33
The data consists of a date string with a slash separator, a time string
with colon separators, and then six numbers separated by white space.
The function fscanf is used for reading formatted ascii data such as
this from a file. Suppose this file is called asc.dat. First, we must open
this file for reading using the fopen command:
c 2000 by CRC Press LLC