Page 145 - Battery Reference Book
P. 145
Alkaline manganese secondary batteries 6/3
Ikalince manganese primary Service capacity remains relatively constant as the dis-
batteries charge schedule is varied. Capacity does not vary as
much with current drain as for the carbon-zinc bat-
Alkaline manganese batteries are a direct competitor tery. Service capacity ranges from several hundred mi-
to the standard carbon-zinc (LeclanchC) battery over liampere hours to up to tens of ampere hours depending
which, in certain applications, they enjoy advantages in on current drain and cut-off voltage.
performance. The primary alkaline manganese battery, The alkaline manganese battery is intended for
which first became available in 1960, represents a applications requiring more power or longer life than
major advance over the standard carbon-zinc battery can be obtained from carbon-zinc batteries. Alkal-
and meets the growing need for a high-rate source of ine manganese batteries contain 50- 100% more total
electrical energy. energy than a conventional carbon-zinc battery of
Alkaline manganese batteries have a high depolar- the same size. Energy densities of alkaline manganese
izing efficiency. On continuous or heavy drains they types are superior to those of carbon-zinc batteries of
perfom very well and have distinct advantages over the same size. In a conventional carbon-zinc battery,
the relatively cheaper carbon-zinc batteries, on a per- heavy current drains and continuous or heavy-duty
formance per unit cost basis. Both alkaline manganese usage impair the efficiency to the extent that only a
and mercury blatteries have a superior operating life small fraction of the built-in energy can be removed.
to carbon-zinc batteries. For applications where volt- The chief advantage of the alkaline manganese bat-
age stability and extremely small size are not of prime tery lies in its ability to work with high efficiency
importance, the alkaline manganese battery may be under continuous or heavy-duty high-drain conditions
considered preferable to the more expensive mercury where the carbon-zinc battery is unsatisfactory. Under
battery. As witlh the mercury battery, the alkaline man- some conditions, alkaline manganese batteries will
ganese battery has a long shelf life, is self-venting provide as much as seven times the service of stan-
and is of corrosion-free construction. Alkaline man- dard carbon-zinc batteries. Discharge characteristics
ganese batteries are capable of providing heavy cur- of alkaline manganese and carbon-zinc batteries are
rents for long periods, which makes them very suitable compared in Figure 6.2.
for applications requiring high surge currents, and can Although alkaline manganese batteries caL out-
'1
operate successfully at temperatures between -20 and perform carbon-zinc batteries in any type of service,
+70°C; in certain cases even higher temperatures can as indicated earlier, they may now show economic
be tolerated. advantage over them at light drains, or under
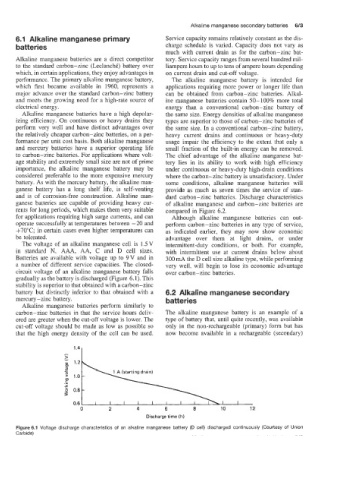
The voltage of an alkaline manganese cell is 1.5 V intermittent-duty conditions, or both. For example,
in standard I\$, AAA, AA, C! and D cell sizes. with intermittent use at current drains below about
Batteries are available with voltage up to 9V and in 300 mA the D cell size alkaline type, while performing
a nuIliber of different service capacities. The closed- very well, will begin to lose its economic advantage
circuit voltage of an alkaline manganese battery falls over carbon-zinc batteries.
gradually as the battery is discharged (Figure 4.1). This
stability is superior to that obtained with a carbon-zinc
battery but dis,tinctly inferior to that obtained with a 6.2 Alkaline manganese secondary
mercury - zinc battery. batteries
Alkaline manganese batteries perform similarly to
carbon-zinc batteries in that the service hours deliv- The alkaline manganese battery is an example of a
ered axe greater when the cut-off voltage is lower. The type of battery that, until quite recently, was available
cut-off voltage should be made as low as possible so only in the non-rechargeable (primary) form but has
that the high energy density of the cell can be used. now become available in a rechargeable (secondary)
1.4,
1
(starting
drain)
1
A
0 2 4 6 8 10
Discharge time (h)
Figure 6.1 Voltage discharge characteristics of an alkaline manganese battery (D cell) discharged continuously (Courtesy of Union
Carbide)