Page 146 - Battery Reference Book
P. 146
6/4 Alkaline manganese batteries
-
>
1 1.5r
1.3-\\ -
-
.-
f - 1.1
a
.- e 0.9 -
0 Alkaline r
-0 - Carbon-zinc 3
- 0.7 , I
u I I I I 1 0
7- Voltage at end of 4 h discharge
't
I I I I I I I I
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
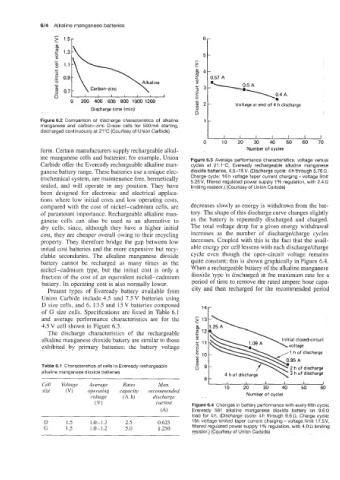
form. Certain manufacturers supply rechargeable alkal- Number of cycles
ine manganese cells and batteries; for example, Union Figure 6.3 Average performance characteristics: voltage versus
Carbide offer the Eveready rechargeable alkaline man- cycles at 21 .I "C, Eveready rechargeable alkaline manganese
ganese battery range. These batteries use a unique elec- dioxide batteries, 4.5-15V. (Discharge cycle: 4 h through 5.76 R.
trochemical system, are maintenance free, hermetically Charge cycle: 16 h voltage taper current charging -voltage limit
sealed, and will operate in any position. They have 5.25V, filtered regulated power supply 1 % regulation, with 2.4 s2
limiting resistor.) (Courtesy of Union Carbide)
been designed for electronic and electrical applica-
tions where low initial costs and low operating costs,
compared with the cost of nickel-cadmium cells, are decreases slowly as energy is withdrawn from the bat-
of paramount importance. Rechargeable alkaline man- tery. The shape of this discharge curve changes slightly
ganese cells can also be used as an alternative to as the battery is repeatedly discharged and charged.
dry cells, since, although they have a higher initial The total voltage drop for a given energy withdrawal
cost, they are cheaper overall owing to their recycling increases as the number of dischargekharge cycles
property. They therefore bridge the gap between low increases. Coupled with this is the fact that the avail-
initial cost batteries and the more expensive but recy- able energy per cell lessens with each dischargekharge
clable secondaries. The alkaline manganese dioxide cycle even though the open-circuit voltage remains
battery cannot be recharged as many times as the quite constant; this is shown graphically in Figure 6.4.
nickel-cadmium type, but the initial cost is only a When a rechargeable battery of the alkaline manganese
fraction of the cost of an equivalent nickel-cadmium dioxide type is discharged at the maximum rate for a
battery. Its operating cost is also normally lower. period of time to remove the rated ampere hour capa-
Present types of Eveready battery available from city and then recharged for the recommended period
Union Carbide include 4.5 and 7.5V batteries using
D size cells, and 6, 13.5 and 15V batteries composed 14-
of G size cells. Specifications are listed in Table 6.1
and average performance characteristics are for the
4.5 V cell shown in Figure 6.3.
The discharge characteristics of the rechargeable
alkaline manganese dioxide battery are similar to those
exhibited by primary batteries; the battery voltage e
'G 10-
3
Table 6.1 Characteristics of cells in Eveready rechargeable G 9- 2 h of discharge
alkaline manganese dioxide batteries 4 h of discharge 3 h of discharge
-
R-
I
J
I
I
1
I
Cell Voltage Average Rates Max. 10 20 30 40 50 60
size (V) operating capacity recommended
voltage (Ah) discharge Number of cycles
(VI current
Figure 6.4 Changes in battery performance with every fifth cycle:
(A) Eveready 561 alkaline manganese dioxide battery on 9.6R
load for 4 h. (Discharge cycle: 4 h through 9.6 R. Charge cycle:
D 1.5 1.0-1.2 2.5 0.625 16h voltage-limited taper current charging - voltage limit 17.5V,
G 1.5 1.0-1.2 5.0 1.250 filtered regulated power supply 1 % regulation, with 4.0 R limiting
resistor.) (Courtesy of Union Carbide)