Page 152 - Battery Reference Book
P. 152
7/4 Carbon-zinc and carbon-zinc chloride primary batteries
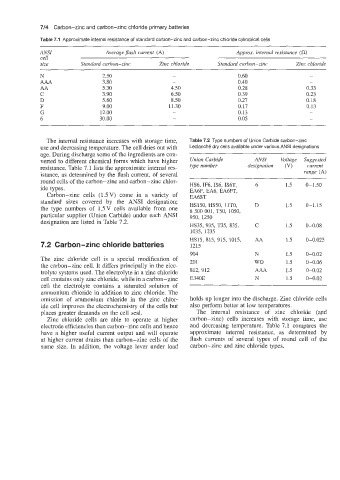
Table 7.1 Approximate internal resistance of standard carbon-zinc and carbon-zinc chloride cylindrical cells
ANSI Average $ash current (A) Approx. internal resistance (a)
cell
size Standard carbon-zinc Zinc chloride Standard carbon-zinc Zinc chloride
N 2.50 - 0.60 -
AAA 3.80 - 0.40 -
AA 5.30 4.50 0.28 0.33
C 3.90 6.50 0.39 0.23
D 5.60 8.50 0.27 0.18
F 9.00 11.30 0.17 0.13
G 12.00 - 0.13 -
6 30.00 - 0.05 -
The internal resistance increases with storage time, Table 7.2 Type numbers of Union Carbide carbon-zinc
use and decreasing temperature. The cell dries out with Leclanche dry cells available under various ANSI designations
age. During discharge some of the ingredients are con-
verted to different chemical forms which have higher Union Carbide ANSI Voltage Suggested
resistance. Table 7.1 lists the approximate internal res- type number designation (V) current
istance, as determined by the flash current, of several range (A)
round cells of the carbon-zinc and carbon-zinc chlor-
ide types. HS6, IF6, IS6, IS6T, 6 1.5 0-1.50
EA6F, EA6, EA6FT,
Carbon-zinc cells (1.5V) come in a variety of EA6ST
standard sizes covered by the ANSI designation;
the type numbers of 1.5 V cells available from one HS150, HS50, 11T0, D 1.5 0-1.15
8 500 001, T50, 1050,
particular supplier (Union Carbide) under each ANSI 950, 1250
designation are listed in Table 7.2.
HS35, 935, T35, 835, C 1.5 0-0.08
1035, 1235
HS15, 815, 915, 1015, AA 1.5 0-0.025
7.2 Carbon-zinc chloride batteries 1215
904 N 1.5 0-0.02
The zinc chloride cell is a special modification of 20 1 wo
the carbon-zinc cell. It differs principally in the elec- 1.5 0-0.06
trolyte systems used. The electrolyte in a zinc chloride 812, 912 AAA 1.5 0-0.02
cell contains only zinc chloride, while in a carbon-zinc E340E N 1.5 0-0.02
cell the electrolyte contains a saturated solution of
ammonium chloride in addition to zinc chloride. The
omission of ammonium chloride in the zinc chlor- holds up longer into the discharge. Zinc chloride cells
ide cell improves the electrochemistry of the cells but also perform better at low temperatures.
places greater demands on the cell seal. The internal resistance of zinc chloride (and
Zinc chloride cells are able to operate at higher carbon-zinc) cells increases with storage time, use
electrode efficiencies than carbon-zinc cells and hence and decreasing temperature. Table 7.1 compares the
have a higher useful current output and will operate approximate internal resistance, as determined by
at higher current drains than carbon-zinc cells of the flash currents of several types of round cell of the
same size. In addition, the voltage lever under load carbon-zinc and zinc chloride types.