Page 504 - Battery Reference Book
P. 504
Standby operation 491%
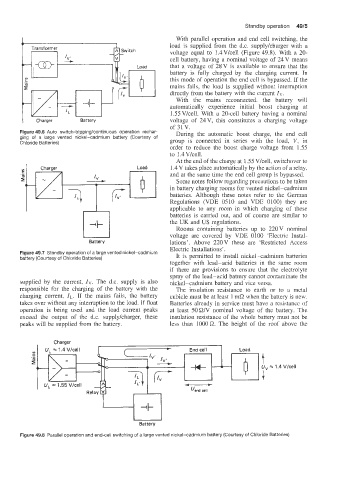
With parallel operation and end cell switching, the
load is supplied from the d.c. supplykharger with a
voltage equal to 1.4V/celi (Figure 49.8). With a 20-
cell battery, having a nominal voltage of 24V means
that a voltage of 28V is available to ensure that the
battery is fully charged by the charging current. In
this mode of operation the end cell is bypassed. If the
mains fails, the load is supplied without intemption
directly from the battery with the current Iv.
With the mains reconnected. the battery will
automatically experience initial boost charging at
1 .55 Vkell. With a 20-cell battery having a nominal
voltage of 24 V, this constitutes a charging voltage
of 31 V.
Figure 49.6 Auto switch-tripping/continuous operation rechar- During the automatic boost charge, the end cell
ging of a large vented nickel-cadmium battery (Courtesy of group is connected in series with the load, V, in
Chloride Batteries)
order to reduce the boost charge voltage from 1.55
to 1.4 Vkell.
At the end of the charge at 1.55 Vkell. switchover to
1.4 V takes place automatically by the action of a relay,
and at the same time the end cell group is bypassed.
Some notes follow regarding precautions to be t&en
in battery charging rooms for vented nickel-cadmium
batteries. Although these notes refer to the Geman
Regulations (VDE 0510 and VDE 0100) they are
applicable to any room in which charging of these
I
batteries is carried out, and of course are similar to
the UK and US regulations.
1-4- Rooms containing batteries up to 220V nominal
voltage are covered by VDE 0100 ‘Electric Instal-
Battery lations’. Above 220V these are ‘Restricted Access
Electric Installations’.
Figure 49.7 Standby operation of a large vented nickel-cadmium It is permitted to install nickel-cadmium batteries
battery (Courtesy of Chloride Batteries)
together with lead-acid batteries in the same room
if there are provisions to ensure that the electrolyte
spray of the lead-acid battery cannot contaminate the
supplied by the current, I”. The d.c. supply is also nickel-cadmium battery and vice versa.
responsible for the charging of the battery with the The insulation resistance to earth or to a metal
charging current, IL. If the mains fails, the battery cubicle must be at least 1 ma when the battery is new.
takes over without any interruption to the load. If float Batteries already in service must have a resistance of
operation is being used and the load current peaks at least 50WV nominal voltage of the battery. The
exceed the output of the d.c. supplykharger, these insulation resistance of the whole battery must not be
peaks will be supplied from the battery. less than 100OQ. The height of the roof above the
f
u, - 1.4 V/cell
I
Battery
Figure 49.8 Padlei operation and end-cell switching of a large vented nickel-cadmium battery (Courtesy of Chloride Batteries)