Page 36 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 36
Conductors and Insulators rn I7
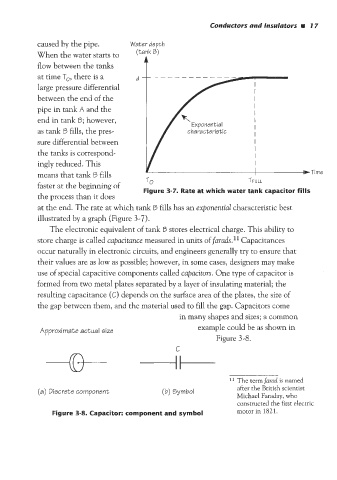
caused by the pipe. Water depth
When the water starts to (tank 6)
flow between the tanks t
at time To, there is a
large pressure differential
between the end of the
pipe in tank A and the
I
end in tank 5; however, I
Exponential
as tank B fills, the pres- characteristic I I
sure differential between I
I
the tanks is correspond- I
ingly reduced. This I
means that tank B fills I
TO TFULL
faster at the beginning of
Figure 3-7. Rate at which water tank capacitor fills
the process than it does
at the end. The rate at which tank 5 fills has an exponential characteristic best
illustrated by a graph (Figure 3-7).
The electronic: equivalent of tank 6 stores electrical charge. This ability to
store charge is called capacitance measured in units of Capacitances
occur naturally in electronic circuits, and engineers generally try to ensure that
their values are as low as possible; however, in some cases, designers may make
use of special capacitive components called capacitors. One type of capacitor is
formed from two metal plates separated by a layer of insulating material; the
resulting capacitance (C) depends on the surface area of the plates, the size of
the gap between them, and the material used to fill the gap. Capacitors come
in many shapes and sizes; a common
example could be as shown in
Approximate actual size Figure 3-8.
++
C
11 The term farad is named
after the British scientist
(a) Discrete cornporient (b) Symbol
Michael Faraday, who
constructed the first electric
Figure 3-8. Capacitor: component and symbol motor in 1821.