Page 51 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 51
32 ChapterFocrr
The Transistor as a Switch
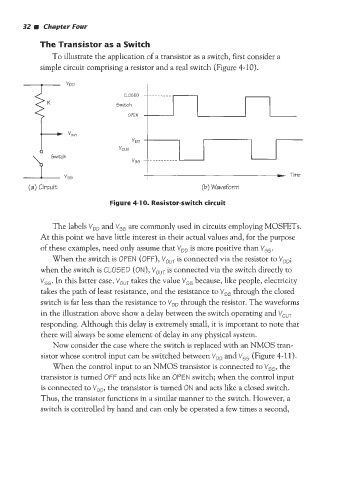
To illustrate the application of a transistor as a switch, first consider a
simple circuit comprising a resistor and a real switch (Figure 4-10).
VDD
CLOBED
Switch
OPEN
Vout
VDD
P v55 I =, Time
VOUT
Switch
(a) Circuit v55 (b) Waveform
Figure 4-10. Resistor-switch circuit
The labels VDD and V,, are commonly used in circuits employing MOSFETs.
At this point we have little interest in their actual values and, for the purpose
of these examples, need only assume that VDD is more positive than v~,.
When the switch is OPEN (OFF), V,,, is connected via the resistor to VDD;
when the switch is CLOSED (ON), Yo,, is connected via the switch directly to
v,~. In this latter case, v,,, takes the value v,, because, like people, electricity
takes the path of least resistance, and the resistance to v,, through the closed
switch is far less than the resistance to VDD through the resistor. The waveforms
in the illustration above show a delay between the switch operating and V,,,
responding. Although this delay is extremely small, it is important to note that
there will always be some element of delay in any physical system.
Now consider the case where the switch is replaced with an NMOS tran-
sistor whose control input can be switched between VDD and V,, (Figure 4-11).
When the control input to an NMOS transistor is connected to V,,, the
transistor is turned OFF and acts like an OPEN switch; when the control input
is connected to VDD, the transistor is turned ON and acts like a closed switch.
Thus, the transistor functions in a similar manner to the switch. However, a
switch is controlled by hand and can only be operated a few times a second,