Page 150 - Encyclopedia Of World History Vol V
P. 150
urbanization 1927
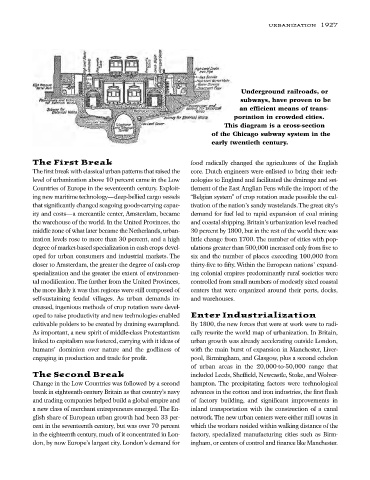
Underground railroads, or
subways, have proven to be
an efficient means of trans-
portation in crowded cities.
This diagram is a cross-section
of the Chicago subway system in the
early twentieth century.
The First Break food radically changed the agricultures of the English
The first break with classical urban patterns that raised the core. Dutch engineers were enlisted to bring their tech-
level of urbanization above 10 percent came in the Low nologies to England and facilitated the drainage and set-
Countries of Europe in the seventeenth century. Exploit- tlement of the East Anglian Fens while the import of the
ing new maritime technology—deep-bellied cargo vessels “Belgian system” of crop rotation made possible the cul-
that significantly changed seagoing goods-carrying capac- tivation of the nation’s sandy wastelands.The great city’s
ity and costs—a mercantile center, Amsterdam, became demand for fuel led to rapid expansion of coal mining
the warehouse of the world. In the United Provinces, the and coastal shipping. Britain’s urbanization level reached
middle zone of what later became the Netherlands,urban- 30 percent by 1800, but in the rest of the world there was
ization levels rose to more than 30 percent, and a high little change from 1700.The number of cities with pop-
degree of market-based specialization in cash crops devel- ulations greater than 500,000 increased only from five to
oped for urban consumers and industrial markets. The six and the number of places exceeding 100,000 from
closer to Amsterdam, the greater the degree of cash-crop thirty-five to fifty.Within the European nations’ expand-
specialization and the greater the extent of environmen- ing colonial empires predominantly rural societies were
tal modification.The further from the United Provinces, controlled from small numbers of modestly sized coastal
the more likely it was that regions were still composed of centers that were organized around their ports, docks,
self-sustaining feudal villages. As urban demands in- and warehouses.
creased, ingenious methods of crop rotation were devel-
oped to raise productivity and new technologies enabled Enter Industrialization
cultivable polders to be created by draining swampland. By 1800, the new forces that were at work were to radi-
As important, a new spirit of middle-class Protestantism cally rewrite the world map of urbanization. In Britain,
linked to capitalism was fostered, carrying with it ideas of urban growth was already accelerating outside London,
humans’ dominion over nature and the godliness of with the main burst of expansion in Manchester, Liver-
engaging in production and trade for profit. pool, Birmingham, and Glasgow, plus a second echelon
of urban areas in the 20,000-to-50,000 range that
The Second Break included Leeds, Sheffield, Newcastle, Stoke, and Wolver-
Change in the Low Countries was followed by a second hampton. The precipitating factors were technological
break in eighteenth-century Britain as that country’s navy advances in the cotton and iron industries, the first flush
and trading companies helped build a global empire and of factory building, and significant improvements in
a new class of merchant entrepreneurs emerged.The En- inland transportation with the construction of a canal
glish share of European urban growth had been 33 per- network.The new urban centers were either mill towns in
cent in the seventeenth century, but was over 70 percent which the workers resided within walking distance of the
in the eighteenth century, much of it concentrated in Lon- factory, specialized manufacturing cities such as Birm-
don, by now Europe’s largest city. London’s demand for ingham, or centers of control and finance like Manchester.