Page 34 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 34
Assessment of Welded Structures by a Structural Multiaxial Fatigue Approach 19
-
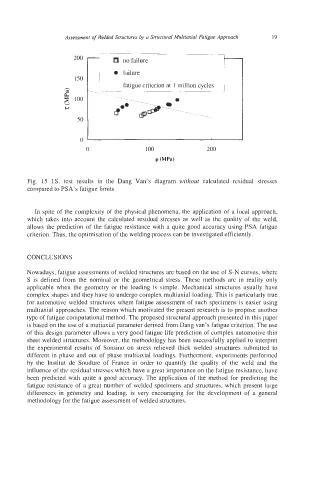
no failure
0 failure
150 _____
_____ fatigue criterion at 1 million cycles
h
Fig. 15 IS. test results in the Dang Van’s diagram without calculated residual stresses
compared to PSA’s fatigue limits
In spite of the complexity of the physical phenomena, the application of a local approach,
which takes into account the calculated residual stresses as well as the quality of the weld,
allows the prediction of the fatigue resistance with a quite good accuracy using PSA fatigue
criterion. Thus, the optimisation of the welding process can be investigated efficiently.
CONCLUSIONS
Nowadays, fatigue assessments of welded structures are based on the use of S-N curves, where
S is defined from the nominal or the geometrical stress. These methods are in reality only
applicable when the geometry or the loading is simple. Mechanical structures usually have
complex shapes and they have to undergo complex multiaxial loading. This is particularly true
for automotive welded structures where fatigue assessment of such specimens is easier using
multiaxial approaches. The reason which motivated the present research is to propose another
type of fatigue computational method. The proposed structural approach presented in this paper
is based on the use of a mutiaxial parameter derived from Dang van’s fatigue criterion. The use
of this design parameter allows a very good fatigue life prediction of complex automotive thin
sheet welded structures. Moreover, the methodology has been successfully applied to interpret
the experimental results of Sonsino on stress relieved thick welded structures submitted to
different in phase and out of phase multiaxial loadings. Furthermore, experiments performed
by the Institut de Soudure of France in order to quantify the quality of the weld and the
influence of the residual stresses which have a great importance on the fatigue resistance, have
been predicted with quite a good accuracy. The application of the method for predicting the
fatigue resistance of a great number of welded specimens and structures, which present large
differences in geometry and loading, is very encouraging for the development of a general
methodology for the fatigue assessment of welded structures.