Page 482 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 482
.
466 1L.T. SAWS ET AL.
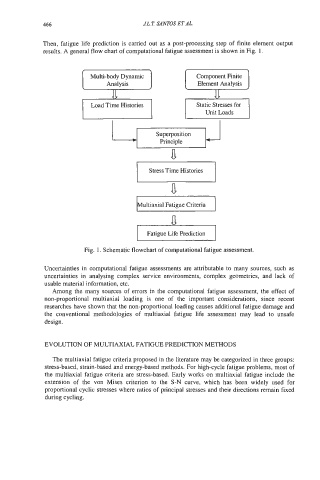
Then, fatigue life prediction is carried out as a post-processing step of finite element output
results. A general flow chart of computational fatigue assessment is shown in Fig. 1.
Analysis Element Analysis
I
Static Stresses for
Load Time Histories
Loads
Unit
Principle
a l
I Stress Time Histories I
a
ultiaxial Fatigue Criteria
Fatigue Life Prediction
Fig. 1. Schematic flowchart of computational fatigue assessment.
Uncertainties in computational fatigue assessments are attributable to many sources, such as
uncertainties in analysing complex service environments, complex geometries, and lack of
usable material information, etc.
Among the many sources of errors in the computational fatigue assessment, the effect of
non-proportional multiaxial loading is one of the important considerations, since recent
researches have shown that the non-proportional loading causes additional fatigue damage and
the conventional methodologies of multiaxial fatigue life assessment may lead to unsafe
design.
EVOLUTION OF MULTIAXIAL FATIGUE PREDICTION METHODS
The multiaxial fatigue criteria proposed in the literature may be categorized in three groups:
stress-based, strain-based and energy-based methods. For high-cycle fatigue problems, most of
the multiaxial fatigue criteria are stress-based. Early works on multiaxial fatigue include the
extension of the von Mises criterion to the S-N curve, which has been widely used for
proportional cyclic stresses where ratios of principal stresses and their directions remain fixed
during cycling.