Page 209 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 209
202 CHAPTER 8 BLOCKCHAIN IN HEALTHCARE: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS
Positioning sensor
(accelerometer)
Blood pressure sensor Airflow sensor
(Sphygmomanometer) (breathing)
Pulse and oxygen in Electrocardiogram
blood sensor (SPO2) sensor (ECG)
Sensor data
Galvanic skin
Body temperature response sensor
sensor
(GSR-sweating)
Wearable sleep Electromyography
tracking device sensor (EMG)
Smart lenses
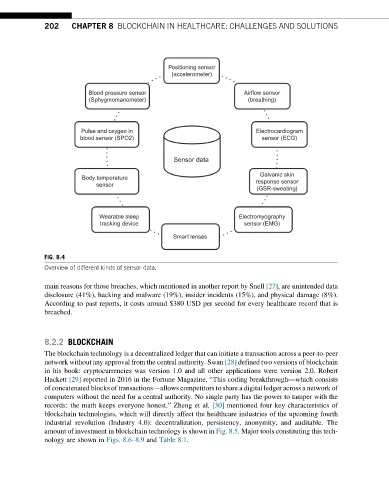
FIG. 8.4
Overview of different kinds of sensor data.
main reasons for those breaches, which mentioned in another report by Snell [27], are unintended data
disclosure (41%), hacking and malware (19%), insider incidents (15%), and physical damage (8%).
According to past reports, it costs around $380 USD per second for every healthcare record that is
breached.
8.2.2 BLOCKCHAIN
The blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger that can initiate a transaction across a peer-to-peer
network without any approval from the central authority. Swan [28] defined two versions of blockchain
in his book: cryptocurrencies was version 1.0 and all other applications were version 2.0. Robert
Hackett [29] reported in 2016 in the Fortune Magazine, “This coding breakthrough—which consists
of concatenated blocks of transactions—allows competitors to share a digital ledger across a network of
computers without the need for a central authority. No single party has the power to tamper with the
records: the math keeps everyone honest.” Zheng et al. [30] mentioned four key characteristics of
blockchain technologies, which will directly affect the healthcare industries of the upcoming fourth
industrial revolution (Industry 4.0): decentralization, persistency, anonymity, and auditable. The
amount of investment in blockchain technology is shown in Fig. 8.5. Major tools constituting this tech-
nology are shown in Figs. 8.6–8.9 and Table 8.1.