Page 206 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 206
8.1 INTRODUCTION 199
Some of the notable opportunities that would be able to revolutionize the healthcare industry with the
integration of the blockchain are as follows [8]:
• Decentralized storage: blockchain stores the information, which is transparent and delivered to third
parties based on the consent of the creator. A decentralized way of storing the information is
keeping multiple copies of that information in multiple places.
• Consent: access, storage, and distribution will be controlled by the global consensus algorithm.
After an autonomous sanction from all available parties, the changes are allowed to be made on
the data.
• Immutability: alteration of any data is impossible. Once data is stored in a particular block, it can
never be changed or modified.
• Increased capacity: With no middleman and less approvals complexity, blockchain is a cost-
effective way of maintaining the privacy of data.
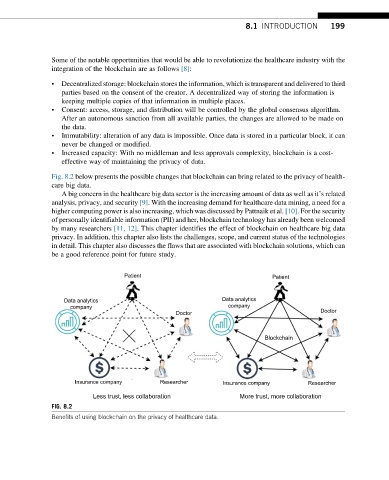
Fig. 8.2 below presents the possible changes that blockchain can bring related to the privacy of health-
care big data.
A big concern in the healthcare big data sector is the increasing amount of data as well as it’s related
analysis, privacy, and security [9]. With the increasing demand for healthcare data mining, a need for a
higher computing power is also increasing, which was discussed by Pattnaik et al. [10]. For the security
of personally identifiable information (PII) and her, blockchain technology has already been welcomed
by many researchers [11, 12]. This chapter identifies the effect of blockchain on healthcare big data
privacy. In addition, this chapter also lists the challenges, scope, and current status of the technologies
in detail. This chapter also discusses the flaws that are associated with blockchain solutions, which can
be a good reference point for future study.
Patient Patient
Data analytics Data analytics
company company
Doctor Doctor
Blockchain
Insurance company Researcher Insurance company Researcher
Less trust, less collaboration More trust, more collaboration
FIG. 8.2
Benefits of using blockchain on the privacy of healthcare data.