Page 228 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 228
8.5 BLOCKCHAIN CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE 221
based on big data analysis and transparent data asset monetization with risk associated management. A
private blockchain is used in this study to initiate a collaborative research environment.
IBM Blockchain: With other blockchain applications, IBM also offers several facilities in the
healthcare domain. The main factor of the IBM healthcare blockchain is the automatic clinical trial
and transparent health record sharing. The detailed advantages are discussed in IBM’s blog titled
“Blockchain in healthcare [84].”
Universal Health Coin: This is a blockchain and AI-based cryptocurrency to exchange data among
stakeholders proposed by Gordon [85]. The user of this system can directly communicate with each
data owner or processor to buy and sell data with this coin, UHC. All these transactions and data
are encrypted and secured by public-private blockchain key.
Genomes: Hahnel [72] proposed another off-chain and on-chain gene information storing platform.
Genomes also provide a platform for securely sharing biological information among third parties.
GENE tokens were introduced by this study as a medium of exchange.
Youbase: Josh [86] proposed a hierarchical deterministic (HD) based wallet. This wallet controls
access to the personal information and contains a tree-like structure with keys. The key advantage is,
due to having several branches (parent and child chains), this Youbase can store data separately
depending on the specific type of information. Data anonymization technique is applied here to comply
with personal data protection regulations.
Peterson et al. [87] proposed a community-based network architecture for a health information ex-
changing mechanism. This study proposed a system where data on a particular node can only be
accessed if data structure and semantics are understood and approved by community members. Patients
ultimately control the privacy and regulation of those shared data. However, direct storing of personal
data is its main drawback.
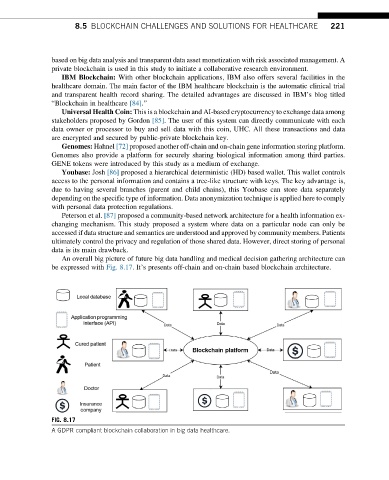
An overall big picture of future big data handling and medical decision gathering architecture can
be expressed with Fig. 8.17. It’s presents off-chain and on-chain based blockchain architecture.
FIG. 8.17
A GDPR compliant blockchain collaboration in big data healthcare.