Page 173 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 173
7.6 Application of external magnet on cancerous solid tumors 171
7.6 Application of external magnet on cancerous
solid tumors
As mentioned magnetic field is one of the most useful external forces for moving
the nano-drug carrier through the body and deliver the drug to the desired place.
One of the drug carrier option is MNPs. MNPs are typically made from iron, nickel,
and cobalt. They are loaded with drugs, coated with biocompatible coatings and are
injected into the human vessel (bloodstream). The loaded particles move through
the vessel and are absorbed by cancerous solid tumor where the magnetic field is
applied. The effect of external magnet on the effectiveness of the cancerous solid
tumor treatment is presented below. The physical parameters that affect the magnetic
drug carriers (MDCs) distribution are studied. The MDCs diffusion coefficients in
the capillary as well as its wall and the tumor tissue are considered as variable and
calculated. These coefficients are functions of MDCs diameter, pore size of capillary
wall, tissue porosity, etc.
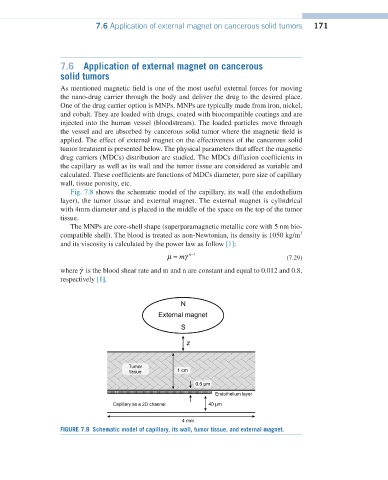
Fig. 7.8 shows the schematic model of the capillary, its wall (the endothelium
layer), the tumor tissue and external magnet. The external magnet is cylindrical
with 4mm diameter and is placed in the middle of the space on the top of the tumor
tissue.
The MNPs are core-shell shape (superparamagnetic metallic core with 5 nm bio-
3
compatible shell). The blood is treated as non-Newtonian, its density is 1050 kg/m
and its viscosity is calculated by the power law as follow [1]:
µ = mγ n 1 (7.29) µ=mγ˙n−1
−
where γ is the blood shear rate and m and n are constant and equal to 0.012 and 0.8, γ˙
respectively [1].
FIGURE 7.8 Schematic model of capillary, its wall, tumor tissue, and external magnet.