Page 220 - Biobehavioral Resilence to Stress
P. 220
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder 197
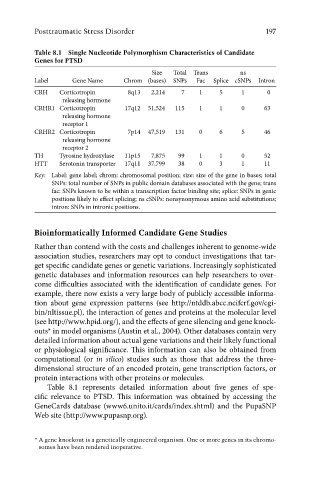
Table 8.1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Characteristics of Candidate
Genes for PTSD
Size Total Trans ns
Label Gene Name Chrom (bases) SNPs Fac Splice cSNPs Intron
CRH Corticotropin 8q13 2,214 7 1 5 1 0
releasing hormone
CRHR1 Corticotropin 17q12 51,524 115 1 1 0 63
releasing hormone
receptor 1
CRHR2 Corticotropin 7p14 47,519 131 0 6 5 46
releasing hormone
receptor 2
TH Tyrosine hydroxylase 11p15 7,875 99 1 1 0 52
HTT Serotonin transporter 17q11 37,799 38 0 3 1 11
Key: Label: gene label; chrom: chromosomal position; size: size of the gene in bases; total
SNPs: total number of SNPs in public domain databases associated with the gene; trans
fac: SNPs known to be within a transcription factor binding site; splice: SNPs in genic
positions likely to eff ect splicing; ns cSNPs: nonsynonymous amino acid substitutions;
intron: SNPs in intronic positions.
Bioinformatically Informed Candidate Gene Studies
Rather than contend with the costs and challenges inherent to genome-wide
association studies, researchers may opt to conduct investigations that tar-
get specific candidate genes or genetic variations. Increasingly sophisticated
genetic databases and information resources can help researchers to over-
come difficulties associated with the identification of candidate genes. For
example, there now exists a very large body of publicly accessible informa-
tion about gene expression patterns (see http://ntddb.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/cgi-
bin/nltissue.pl), the interaction of genes and proteins at the molecular level
(see http://www.hpid.org/), and the effects of gene silencing and gene knock-
outs* in model organisms (Austin et al., 2004). Other databases contain very
detailed information about actual gene variations and their likely functional
or physiological signifi cance. This information can also be obtained from
computational (or in silico) studies such as those that address the three-
dimensional structure of an encoded protein, gene transcription factors, or
protein interactions with other proteins or molecules.
Table 8.1 represents detailed information about five genes of spe-
cific relevance to PTSD. This information was obtained by accessing the
GeneCards database (www6.unito.it/cards/index.shtml) and the PupaSNP
Web site (http://www.pupasnp.org).
* A gene knockout is a genetically engineered organism. One or more genes in its chromo-
somes have been rendered inoperative.
1/22/2008 9:36:20 PM
CRC_71777_Ch008.indd 197
CRC_71777_Ch008.indd 197 1/22/2008 9:36:20 PM