Page 37 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 37
1.5 Directed Evolution of Peroxidases and Peroxygenases 13
Extracellular (a)
Medium
Glycosylation
Side chain SP SP
Core Cellular wall
Polypeptide SP
Pre-leader
SP
Pro-leader
VP
KEX2
Golgi
STE13
Mature Vp
Ribosome VP
KREAEA
mRNA
EAEA
Cytoplasm
α-pre α-pre αvр 2 (b) α-pre α-pre αvр 2 (c)
Peptidase KEX2STE13 Peptidase KEX2
...AKEEGVSLEKR EAEA ATCDDGRTTA... ...AKEEGVSLEKR ATCDDGRTTA...
KEX2STE13 KEX2
Correctly processed
(1) Suggested processing (2) AIternative processing
truncated variants
EAEA
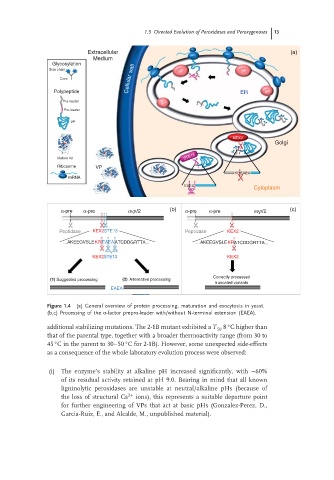
Figure 1.4 (a) General overview of protein processing, maturation and exocytosis in yeast.
(b,c) Processing of the α-factor prepro-leader with/without N-terminal extension (EAEA).
◦
additional stabilizing mutations. The 2-1B mutant exhibited a T 8 C higher than
50
that of the parental type, together with a broader thermoactivity range (from 30 to
◦
◦
45 C in the parent to 30–50 C for 2-1B). However, some unexpected side-effects
as a consequence of the whole laboratory evolution process were observed:
(i) The enzyme’s stability at alkaline pH increased significantly, with ∼60%
of its residual activity retained at pH 9.0. Bearing in mind that all known
ligninolytic peroxidases are unstable at neutral/alkaline pHs (because of
the loss of structural Ca 2+ ions), this represents a suitable departure point
for further engineering of VPs that act at basic pHs (Gonzalez-Perez, D.,
Garcia-Ruiz, E., and Alcalde, M., unpublished material).