Page 221 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 221
204 Chapter Seven
7.7 Alcohols in CI Engine
Although the physical and thermodynamic characteristics of alcohols do
not make them particularly suitable for compression ignition (CI)
engines, with certain modifications, however, they can also be used in
CI engines. In heavy vehicles powered by CI engines, ethanol carbure-
tion can be employed for bi-fuel operation of the engine with proportional
savings in diesel oil. The various methods for using alcohols with diesel
are fumigation, dual injection, and alcohol–diesel emulsions.
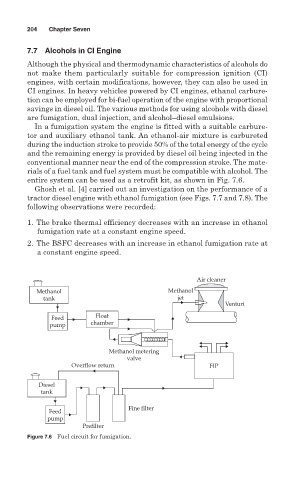
In a fumigation system the engine is fitted with a suitable carbure-
tor and auxiliary ethanol tank. An ethanol-air mixture is carbureted
during the induction stroke to provide 50% of the total energy of the cycle
and the remaining energy is provided by diesel oil being injected in the
conventional manner near the end of the compression stroke. The mate-
rials of a fuel tank and fuel system must be compatible with alcohol. The
entire system can be used as a retrofit kit, as shown in Fig. 7.6.
Ghosh et al. [4] carried out an investigation on the performance of a
tractor diesel engine with ethanol fumigation (see Figs. 7.7 and 7.8). The
following observations were recorded:
1. The brake thermal efficiency decreases with an increase in ethanol
fumigation rate at a constant engine speed.
2. The BSFC decreases with an increase in ethanol fumigation rate at
a constant engine speed.
Air cleaner
Methanol Methanol
tank jet
Venturi
Float
Feed
pump chamber
Methanol metering
valve
Overflow return FIP
Diesel
tank
Fine filter
Feed
pump
Prefilter
Figure 7.6 Fuel circuit for fumigation.