Page 226 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 226
Ethanol and Methanol as Fuels in Internal Combustion Engines 209
IC engine fuels. Availability from indigenous sources, ease of handling,
low emission, and high thermal efficiency obtainable with its use make
methanol a logical alternative fuel for vehicular engines.
7.8.1 Production of methanol
Methanol can be produced from resources such as coal, natural gas, oil
shell, and farm waste, which are abundant worldwide. But methanol
from natural gas is unlikely to provide a large greenhouse benefit, not
more than a 10% reduction in emissions with quite optimistic assump-
tions. It is not considered as a main raw material to produce methanol.
For countries having vast reserves of coal but small oil deposits,
methanol from coal can provide an indigenous substitute to oil. But this
method has an adverse effect on greenhouse gases and is very expen-
sive, requiring capital investments that can increase the price by 50%.
In India, there is an abundant production of sugarcane. The govern-
ment can divert this feedstock to produce methanol. The production of
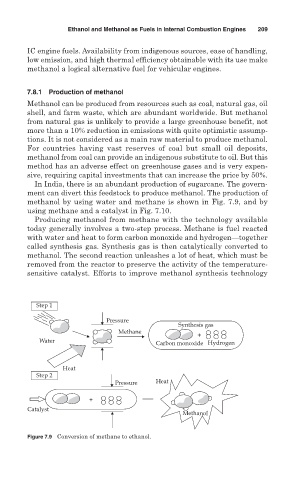
methanol by using water and methane is shown in Fig. 7.9, and by
using methane and a catalyst in Fig. 7.10.
Producing methanol from methane with the technology available
today generally involves a two-step process. Methane is fuel reacted
with water and heat to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen—together
called synthesis gas. Synthesis gas is then catalytically converted to
methanol. The second reaction unleashes a lot of heat, which must be
removed from the reactor to preserve the activity of the temperature-
sensitive catalyst. Efforts to improve methanol synthesis technology
Step 1
Pressure
Synthesis gas
Methane
+
Water Carbon monoxide Hydrogen
Heat
Step 2
Pressure Heat
+
Catalyst
Methanol
Figure 7.9 Conversion of methane to ethanol.