Page 368 - Biofuels for a More Sustainable Future
P. 368
324 Biofuels for a More Sustainable Future
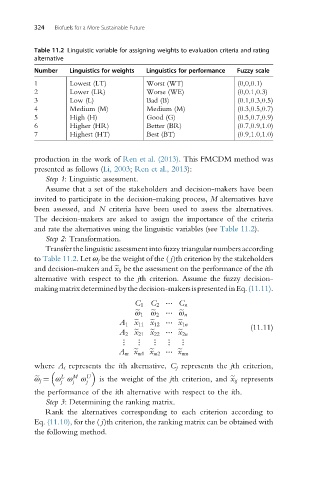
Table 11.2 Linguistic variable for assigning weights to evaluation criteria and rating
alternative
Number Linguistics for weights Linguistics for performance Fuzzy scale
1 Lowest (LT) Worst (WT) (0,0,0.1)
2 Lower (LR) Worse (WE) (0,0.1,0.3)
3 Low (L) Bad (B) (0.1,0.3,0.5)
4 Medium (M) Medium (M) (0.3,0.5,0.7)
5 High (H) Good (G) (0.5,0.7,0.9)
6 Higher (HR) Better (BR) (0.7,0.9,1.0)
7 Highest (HT) Best (BT) (0.9,1.0,1.0)
production in the work of Ren et al. (2013). This FMCDM method was
presented as follows (Li, 2003; Ren et al., 2013):
Step 1: Linguistic assessment.
Assume that a set of the stakeholders and decision-makers have been
invited to participate in the decision-making process, M alternatives have
been assessed, and N criteria have been used to assess the alternatives.
The decision-makers are asked to assign the importance of the criteria
and rate the alternatives using the linguistic variables (see Table 11.2).
Step 2: Transformation.
Transfer the linguistic assessment into fuzzy triangular numbers according
to Table 11.2. Let ω j be the weight of the ( j)th criterion by the stakeholders
and decision-makers and e ij be the assessment on the performance of the ith
x
alternative with respect to the jth criterion. Assume the fuzzy decision-
makingmatrixdeterminedbythedecision-makersispresentedinEq.(11.11).
C 1 C 2 ⋯ C n
e ω 1 ω 2 ⋯ e ω n
e
x
x
x
A 1 e 11 e 12 ⋯ e 1n
(11.11)
x
x
x
A 2 e 21 e 22 ⋯ e 2n
⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
A m ex m1 ex m2 ⋯ ex mn
where A i represents the ith alternative, C j represents the jth criterion,
e ω j ¼ ω ω M ω U is the weight of the jth criterion, and e ij represents
L
x
j j j
the performance of the ith alternative with respect to the ith.
Step 3: Determining the ranking matrix.
Rank the alternatives corresponding to each criterion according to
Eq. (11.10), for the ( j)th criterion, the ranking matrix can be obtained with
the following method.