Page 207 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 207
184 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
Postgasification
Product gas cleaning
+ tar
Biomass Gasifier tar + dust Clean gas
scrubbing
catalytic tar
(A) reduction
Gasifying
agent
Tar-free
Gasifier product gas
Biomass
with in situ Dust cleaning Clean gas
tar removal
(B)
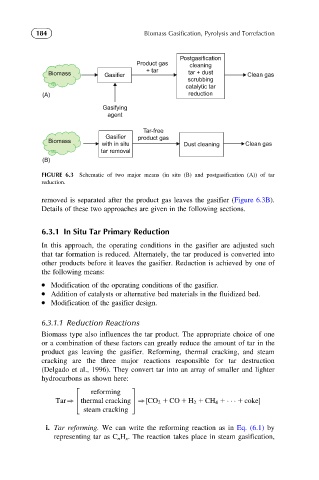
FIGURE 6.3 Schematic of two major means (in situ (B) and postgasification (A)) of tar
reduction.
removed is separated after the product gas leaves the gasifier (Figure 6.3B).
Details of these two approaches are given in the following sections.
6.3.1 In Situ Tar Primary Reduction
In this approach, the operating conditions in the gasifier are adjusted such
that tar formation is reduced. Alternately, the tar produced is converted into
other products before it leaves the gasifier. Reduction is achieved by one of
the following means:
Modification of the operating conditions of the gasifier.
Addition of catalysts or alternative bed materials in the fluidized bed.
Modification of the gasifier design.
6.3.1.1 Reduction Reactions
Biomass type also influences the tar product. The appropriate choice of one
or a combination of these factors can greatly reduce the amount of tar in the
product gas leaving the gasifier. Reforming, thermal cracking, and steam
cracking are the three major reactions responsible for tar destruction
(Delgado et al., 1996). They convert tar into an array of smaller and lighter
hydrocarbons as shown here:
2 3
reforming
Tar. thermal cracking .½CO 2 1 CO 1 H 2 1 CH 4 1 1 coke
5
4
steam cracking
i. Tar reforming. We can write the reforming reaction as in Eq. (6.1) by
representing tar as C n H x . The reaction takes place in steam gasification,