Page 211 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 211
188 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
Biomass
20 C
Drying
100 C
Pyrolysis 500-700 C
Air Air
Combustion 1000-1400 C
Gasification
Temperature (C)
Gas Gas
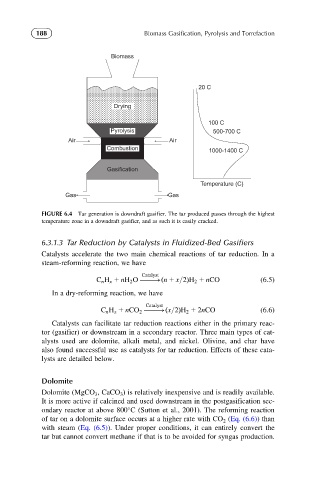
FIGURE 6.4 Tar generation is downdraft gasifier. The tar produced passes through the highest
temperature zone in a downdraft gasifier, and as such it is easily cracked.
6.3.1.3 Tar Reduction by Catalysts in Fluidized-Bed Gasifiers
Catalysts accelerate the two main chemical reactions of tar reduction. In a
steam-reforming reaction, we have
Catalyst
C n H x 1 nH 2 O !ðn 1 x=2ÞH 2 1 nCO (6.5)
In a dry-reforming reaction, we have
Catalyst
C n H x 1 nCO 2 !ðx=2ÞH 2 1 2nCO (6.6)
Catalysts can facilitate tar reduction reactions either in the primary reac-
tor (gasifier) or downstream in a secondary reactor. Three main types of cat-
alysts used are dolomite, alkali metal, and nickel. Olivine, and char have
also found successful use as catalysts for tar reduction. Effects of these cata-
lysts are detailed below.
Dolomite
Dolomite (MgCO 3 , CaCO 3 ) is relatively inexpensive and is readily available.
It is more active if calcined and used downstream in the postgasification sec-
ondary reactor at above 800 C (Sutton et al., 2001). The reforming reaction
of tar on a dolomite surface occurs at a higher rate with CO 2 (Eq. (6.6)) than
with steam (Eq. (6.5)). Under proper conditions, it can entirely convert the
tar but cannot convert methane if that is to be avoided for syngas production.