Page 214 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 214
Chapter | 6 Tar Production and Destruction 191
Biomass
Tar formation
Gas, tar
Pyrolysis Tar
200 – 500°C
Reduction
Combustion
1000°C
Air Ash
Temperature
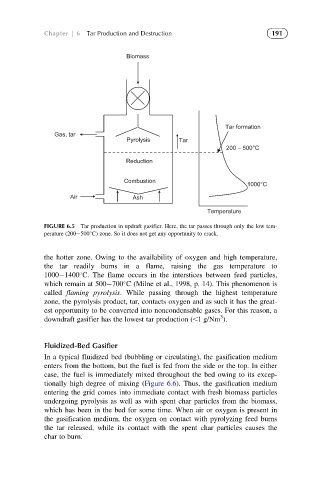
FIGURE 6.5 Tar production in updraft gasifier. Here, the tar passes through only the low tem-
perature (200 500 C) zone. So it does not get any opportunity to crack.
the hotter zone. Owing to the availability of oxygen and high temperature,
the tar readily burns in a flame, raising the gas temperature to
1000 1400 C. The flame occurs in the interstices between feed particles,
which remain at 500 700 C (Milne et al., 1998, p. 14). This phenomenon is
called flaming pyrolysis. While passing through the highest temperature
zone, the pyrolysis product, tar, contacts oxygen and as such it has the great-
est opportunity to be converted into noncondensable gases. For this reason, a
3
downdraft gasifier has the lowest tar production (,1 g/Nm ).
Fluidized-Bed Gasifier
In a typical fluidized bed (bubbling or circulating), the gasification medium
enters from the bottom, but the fuel is fed from the side or the top. In either
case, the fuel is immediately mixed throughout the bed owing to its excep-
tionally high degree of mixing (Figure 6.6). Thus, the gasification medium
entering the grid comes into immediate contact with fresh biomass particles
undergoing pyrolysis as well as with spent char particles from the biomass,
which has been in the bed for some time. When air or oxygen is present in
the gasification medium, the oxygen on contact with pyrolyzing feed burns
the tar released, while its contact with the spent char particles causes the
char to burn.