Page 38 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 38
Chapter | 1 Introduction 17
plant is 745 g/kWh compared to 770 g/kWh from a combustion-based sub-
critical pulverized coal (PC) plant (Termuehlen and Emsperger, 2003, p. 23).
Sequestration of CO 2 could become an important requirement for new
power plants. On that note, a gasification-based power plant has an advantage
over a conventional combustion-based PC power plant because CO 2 is more
concentrated in the flue gas from an IGCC plant making it easier to sequestrate
than that from a conventional PC plant where CO 2 is diluted with nitrogen.
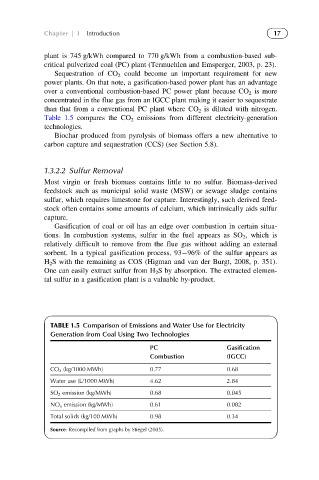
Table 1.5 compares the CO 2 emissions from different electricity-generation
technologies.
Biochar produced from pyrolysis of biomass offers a new alternative to
carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) (see Section 5.8).
1.3.2.2 Sulfur Removal
Most virgin or fresh biomass contains little to no sulfur. Biomass-derived
feedstock such as municipal solid waste (MSW) or sewage sludge contains
sulfur, which requires limestone for capture. Interestingly, such derived feed-
stock often contains some amounts of calcium, which intrinsically aids sulfur
capture.
Gasification of coal or oil has an edge over combustion in certain situa-
tions. In combustion systems, sulfur in the fuel appears as SO 2 , which is
relatively difficult to remove from the flue gas without adding an external
sorbent. In a typical gasification process, 93 96% of the sulfur appears as
H 2 S with the remaining as COS (Higman and van der Burgt, 2008, p. 351).
One can easily extract sulfur from H 2 S by absorption. The extracted elemen-
tal sulfur in a gasification plant is a valuable by-product.
TABLE 1.5 Comparison of Emissions and Water Use for Electricity
Generation from Coal Using Two Technologies
PC Gasification
Combustion (IGCC)
CO 2 (kg/1000 MWh) 0.77 0.68
Water use (L/1000 MWh) 4.62 2.84
SO 2 emission (kg/MWh) 0.68 0.045
NO x emission (kg/MWh) 0.61 0.082
Total solids (kg/100 MWh) 0.98 0.34
Source: Recompiled from graphs by Stiegel (2005).