Page 65 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 65
44 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
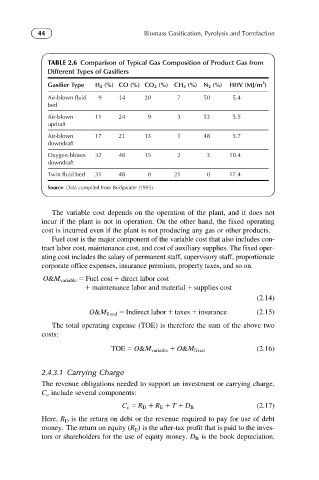
TABLE 2.6 Comparison of Typical Gas Composition of Product Gas from
Different Types of Gasifiers
3
Gasifier Type H 2 (%) CO (%) CO 2 (%) CH 4 (%) N 2 (%) HHV (MJ/m )
Air-blown fluid 9 14 20 7 50 5.4
bed
Air-blown 11 24 9 3 53 5.5
updraft
Air-blown 17 21 13 1 48 5.7
downdraft
Oxygen-blown 32 48 15 2 3 10.4
downdraft
Twin fluid bed 31 48 0 21 0 17.4
Source: Data compiled from Bridgwater (1995).
The variable cost depends on the operation of the plant, and it does not
incur if the plant is not in operation. On the other hand, the fixed operating
cost is incurred even if the plant is not producing any gas or other products.
Fuel cost is the major component of the variable cost that also includes con-
tract labor cost, maintenance cost, and cost of auxiliary supplies. The fixed oper-
ating cost includes the salary of permanent staff, supervisory staff, proportionate
corporate office expenses, insurance premium, property taxes, and so on.
O&M variable 5 Fuel cost 1 direct labor cost
1 maintenance labor and material 1 supplies cost
(2.14)
O&M fixed 5 Indirect labor 1 taxes 1 insurance (2.15)
The total operating expense (TOE) is therefore the sum of the above two
costs:
TOE 5 O&M variable 1 O&M fixed (2.16)
2.4.3.1 Carrying Charge
The revenue obligations needed to support an investment or carrying charge,
C c include several components:
C c 5 R D 1 R E 1 T 1 D B (2.17)
Here, R D is the return on debt or the revenue required to pay for use of debt
money. The return on equity (R E ) is the after-tax profit that is paid to the inves-
tors or shareholders for the use of equity money. D B is the book depreciation.