Page 75 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 75
54 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
Methane is an important constituent of the landfill gas. It is also a power-
ful greenhouse gas (,21 times stronger than CO 2 ) that is often burnt in a
flare or utilized in a gas engine or in similar energy applications. Anaerobic
digestion is very popular in farming communities, where animal excreta are
collected and stored because the gas produced can be collected in a gas
holder for use in cooking and heating while the residual solid can be used as
fertilizer.
3.3 STRUCTURE OF BIOMASS
Biomass is a complex mixture of organic materials such as carbohydrates,
fats, and proteins, along with small amounts of minerals such as sodium,
phosphorus, calcium, and iron. The main components of plant biomass are
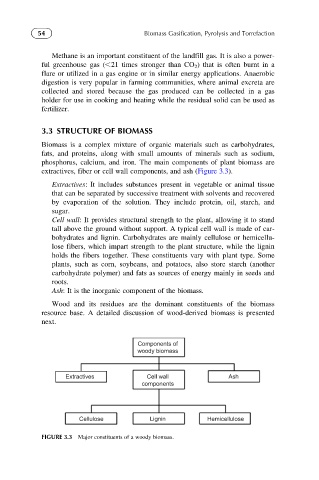
extractives, fiber or cell wall components, and ash (Figure 3.3).
Extractives: It includes substances present in vegetable or animal tissue
that can be separated by successive treatment with solvents and recovered
by evaporation of the solution. They include protein, oil, starch, and
sugar.
Cell wall: It provides structural strength to the plant, allowing it to stand
tall above the ground without support. A typical cell wall is made of car-
bohydrates and lignin. Carbohydrates are mainly cellulose or hemicellu-
lose fibers, which impart strength to the plant structure, while the lignin
holds the fibers together. These constituents vary with plant type. Some
plants, such as corn, soybeans, and potatoes, also store starch (another
carbohydrate polymer) and fats as sources of energy mainly in seeds and
roots.
Ash: It is the inorganic component of the biomass.
Wood and its residues are the dominant constituents of the biomass
resource base. A detailed discussion of wood-derived biomass is presented
next.
Components of
woody biomass
Extractives Cell wall Ash
components
Cellulose Lignin Hemicellulose
FIGURE 3.3 Major constituents of a woody biomass.