Page 221 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 221
200 MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN
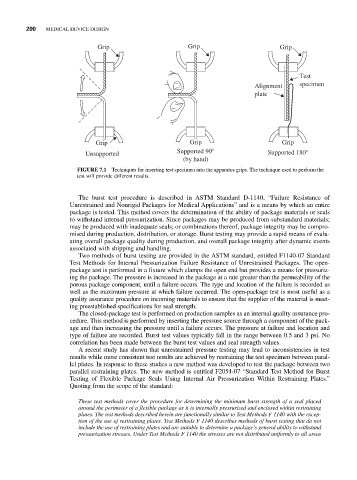
Grip Grip Grip
Test
Alignment specimen
plate
Grip Grip Grip
Supported 90° Supported 180°
Unsupported
(by hand)
FIGURE 7.1 Techniques for inserting test specimen into the apparatus grips. The technique used to perform the
test will provide different results.
The burst test procedure is described in ASTM Standard D-1140, “Failure Resistance of
Unrestrained and Nonrigid Packages for Medical Applications” and is a means by which an entire
package is tested. This method covers the determination of the ability of package materials or seals
to withstand internal pressurization. Since packages may be produced from substandard materials;
may be produced with inadequate seals; or combinations thereof, package integrity may be compro-
mised during production, distribution, or storage. Burst testing may provide a rapid means of evalu-
ating overall package quality during production, and overall package integrity after dynamic events
associated with shipping and handling.
Two methods of burst testing are provided in the ASTM standard, entitled F1140-07 Standard
Test Methods for Internal Pressurization Failure Resistance of Unrestrained Packages. The open-
package test is performed in a fixture which clamps the open end but provides a means for pressuriz-
ing the package. The pressure is increased in the package at a rate greater than the permeability of the
porous package component, until a failure occurs. The type and location of the failure is recorded as
well as the maximum pressure at which failure occurred. The open-package test is most useful as a
quality assurance procedure on incoming materials to ensure that the supplier of the material is meet-
ing preestablished specifications for seal strength.
The closed-package test is performed on production samples as an internal quality assurance pro-
cedure. This method is performed by inserting the pressure source through a component of the pack-
age and then increasing the pressure until a failure occurs. The pressure at failure and location and
type of failure are recorded. Burst test values typically fall in the range between 0.5 and 3 psi. No
correlation has been made between the burst test values and seal strength values.
A recent study has shown that unrestrained pressure testing may lead to inconsistencies in test
results while more consistent test results are achieved by restraining the test specimen between paral-
lel plates. In response to these studies a new method was developed to test the package between two
parallel restraining plates. The new method is entitled F2054-07 “Standard Test Method for Burst
Testing of Flexible Package Seals Using Internal Air Pressurization Within Restraining Plates.”
Quoting from the scope of the standard:
These test methods cover the procedure for determining the minimum burst strength of a seal placed
around the perimeter of a flexible package as it is internally pressurized and enclosed within restraining
plates. The test methods described herein are functionally similar to Test Methods F 1140 with the excep-
tion of the use of restraining plates. Test Methods F 1140 describes methods of burst testing that do not
include the use of restraining plates and are suitable to determine a package’s general ability to withstand
pressurization stresses. Under Test Methods F 1140 the stresses are not distributed uniformly to all areas