Page 44 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 44
FDA MEDICAL DEVICE REQUIREMENTS 23
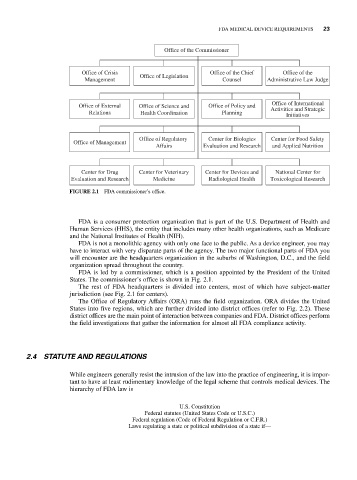
Office of the Commissioner
Office of Crisis Office of the Chief Office of the
Office of Legislation
Management Counsel Administrative Law Judge
Office of International
Office of External Office of Science and Office of Policy and Activities and Strategic
Relations Health Coordination Planning Initiatives
Office of Regulatory Center for Biologics Center for Food Safety
Office of Management
Affairs Evaluation and Research and Applied Nutrition
Center for Drug Center for Veterinary Center for Devices and National Center for
Evaluation and Research Medicine Radiological Health Toxicological Research
FIGURE 2.1 FDA commissioner’s office.
FDA is a consumer protection organization that is part of the U.S. Department of Health and
Human Services (HHS), the entity that includes many other health organizations, such as Medicare
and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
FDA is not a monolithic agency with only one face to the public. As a device engineer, you may
have to interact with very disparate parts of the agency. The two major functional parts of FDA you
will encounter are the headquarters organization in the suburbs of Washington, D.C., and the field
organization spread throughout the country.
FDA is led by a commissioner, which is a position appointed by the President of the United
States. The commissioner’s office is shown in Fig. 2.1.
The rest of FDA headquarters is divided into centers, most of which have subject-matter
jurisdiction (see Fig. 2.1 for centers).
The Office of Regulatory Affairs (ORA) runs the field organization. ORA divides the United
States into five regions, which are further divided into district offices (refer to Fig. 2.2). These
district offices are the main point of interaction between companies and FDA. District offices perform
the field investigations that gather the information for almost all FDA compliance activity.
2.4 STATUTE AND REGULATIONS
While engineers generally resist the intrusion of the law into the practice of engineering, it is impor-
tant to have at least rudimentary knowledge of the legal scheme that controls medical devices. The
hierarchy of FDA law is
U.S. Constitution
Federal statutes (United States Code or U.S.C.)
Federal regulation (Code of Federal Regulation or C.F.R.)
Laws regulating a state or political subdivision of a state if—