Page 83 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 83
62 MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN
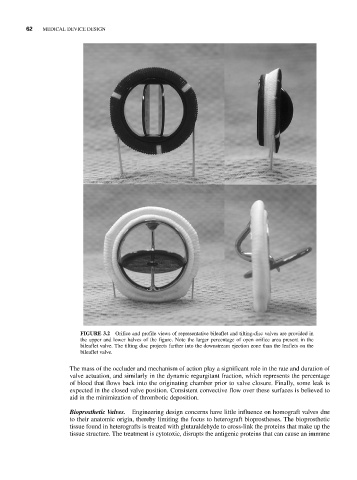
FIGURE 3.2 Orifice and profile views of representative bileaflet and tilting-disc valves are provided in
the upper and lower halves of the figure. Note the larger percentage of open orifice area present in the
bileaflet valve. The tilting disc projects farther into the downstream ejection zone than the leaflets on the
bileaflet valve.
The mass of the occluder and mechanism of action play a significant role in the rate and duration of
valve actuation, and similarly in the dynamic regurgitant fraction, which represents the percentage
of blood that flows back into the originating chamber prior to valve closure. Finally, some leak is
expected in the closed valve position. Consistent convective flow over these surfaces is believed to
aid in the minimization of thrombotic deposition.
Bioprosthetic Valves. Engineering design concerns have little influence on homograft valves due
to their anatomic origin, thereby limiting the focus to heterograft bioprostheses. The bioprosthetic
tissue found in heterografts is treated with glutaraldehyde to cross-link the proteins that make up the
tissue structure. The treatment is cytotoxic, disrupts the antigenic proteins that can cause an immune