Page 238 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 238
216 Cha pte r Se v e n
HO CH OH HO CH OH
2
2
HO OH
O O O
HO HO
OH OH
O O O O
OH CH 2 OH
CH 2 OH OH
n
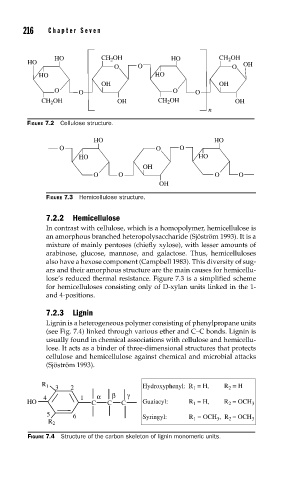
FIGURE 7.2 Cellulose structure.
HO HO
O O O
HO HO
OH
O O O O
OH
FIGURE 7.3 Hemicellulose structure.
7.2.2 Hemicellulose
In contrast with cellulose, which is a homopolymer, hemicellulose is
an amorphous branched heteropolysaccharide (Sjöström 1993). It is a
mixture of mainly pentoses (chiefly xylose), with lesser amounts of
arabinose, glucose, mannose, and galactose. Thus, hemicelluloses
also have a hexose component (Campbell 1983). This diversity of sug-
ars and their amorphous structure are the main causes for hemicellu-
lose’s reduced thermal resistance. Figure 7.3 is a simplified scheme
for hemicelluloses consisting only of D-xylan units linked in the 1-
and 4-positions.
7.2.3 Lignin
Lignin is a heterogeneous polymer consisting of phenylpropane units
(see Fig. 7.4) linked through various ether and C–C bonds. Lignin is
usually found in chemical associations with cellulose and hemicellu-
lose. It acts as a binder of three-dimensional structures that protects
cellulose and hemicellulose against chemical and microbial attacks
(Sjöström 1993).
R 1 3 2 Hydroxyphenyl: R = H, R = H
1
2
4 1
HO C C C Guaiacyl: R 1 = H, R = OCH 3
2
5 6 Syringyl: R = OCH , R = OCH
R 2 1 3 2 3
FIGURE 7.4 Structure of the carbon skeleton of lignin monomeric units.