Page 394 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 394
Extraction, Refining, and Stabilization of Edible Oils 371
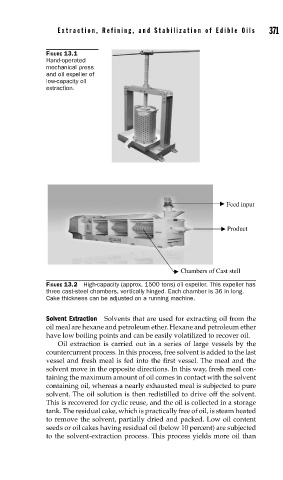
FIGURE 13.1
Hand-operated
mechanical press
and oil expeller of
low-capacity oil
extraction.
Feed input
Product
Chambers of Cast stell
FIGURE 13.2 High-capacity (approx. 1500 tons) oil expeller. This expeller has
three cast-steel chambers, vertically hinged. Each chamber is 36 in long.
Cake thickness can be adjusted on a running machine.
Solvent Extraction Solvents that are used for extracting oil from the
oil meal are hexane and petroleum ether. Hexane and petroleum ether
have low boiling points and can be easily volatilized to recover oil.
Oil extraction is carried out in a series of large vessels by the
countercurrent process. In this process, free solvent is added to the last
vessel and fresh meal is fed into the first vessel. The meal and the
solvent move in the opposite directions. In this way, fresh meal con-
taining the maximum amount of oil comes in contact with the solvent
containing oil, whereas a nearly exhausted meal is subjected to pure
solvent. The oil solution is then redistilled to drive off the solvent.
This is recovered for cyclic reuse, and the oil is collected in a storage
tank. The residual cake, which is practically free of oil, is steam heated
to remove the solvent, partially dried and packed. Low oil content
seeds or oil cakes having residual oil (below 10 percent) are subjected
to the solvent-extraction process. This process yields more oil than