Page 38 - Boiler Operator’s Handbook
P. 38
Operating Wisely 23
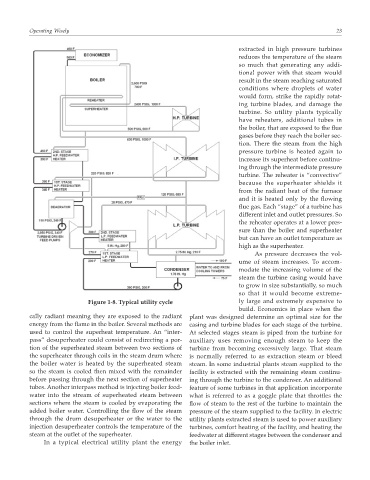
extracted in high pressure turbines
reduces the temperature of the steam
so much that generating any addi-
tional power with that steam would
result in the steam reaching saturated
conditions where droplets of water
would form, strike the rapidly rotat-
ing turbine blades, and damage the
turbine. So utility plants typically
have reheaters, additional tubes in
the boiler, that are exposed to the flue
gases before they reach the boiler sec-
tion. There the steam from the high
pressure turbine is heated again to
increase its superheat before continu-
ing through the intermediate pressure
turbine. The reheater is “convective”
because the superheater shields it
from the radiant heat of the furnace
and it is heated only by the flowing
flue gas. Each “stage” of a turbine has
different inlet and outlet pressures. So
the reheater operates at a lower pres-
sure than the boiler and superheater
but can have an outlet temperature as
high as the superheater.
As pressure decreases the vol-
ume of steam increases. To accom-
modate the increasing volume of the
steam the turbine casing would have
to grow in size substantially, so much
so that it would become extreme-
Figure 1-8. Typical utility cycle ly large and extremely expensive to
build. Economics in place when the
cally radiant meaning they are exposed to the radiant plant was designed determine an optimal size for the
energy from the flame in the boiler. Several methods are casing and turbine blades for each stage of the turbine.
used to control the superheat temperature. An “inter- At selected stages steam is piped from the turbine for
pass” desuperheater could consist of redirecting a por- auxiliary uses removing enough steam to keep the
tion of the superheated steam between two sections of turbine from becoming excessively large. That steam
the superheater through coils in the steam drum where is normally referred to as extraction steam or bleed
the boiler water is heated by the superheated steam steam. In some industrial plants steam supplied to the
so the steam is cooled then mixed with the remainder facility is extracted with the remaining steam continu-
before passing through the next section of superheater ing through the turbine to the condenser. An additional
tubes. Another interpass method is injecting boiler feed- feature of some turbines in that application incorporate
water into the stream of superheated steam between what is referred to as a goggle plate that throttles the
sections where the steam is cooled by evaporating the flow of steam to the rest of the turbine to maintain the
added boiler water. Controlling the flow of the steam pressure of the steam supplied to the facility. In electric
through the drum desuperheater or the water to the utility plants extracted steam is used to power auxiliary
injection desuperheater controls the temperature of the turbines, comfort heating of the facility, and heating the
steam at the outlet of the superheater. feedwater at different stages between the condenser and
In a typical electrical utility plant the energy the boiler inlet.