Page 243 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 243
228 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
WHERE WASTE HEAT CAN BE USED when the energy wouldn’t be needed thereby
wasting it. Using the boiler for waste heat recov-
A suitable use for waste energy is critical to ery provides an uninterruptable use of this ener-
any waste heat recovery project because it doesn’t gy.
matter how much energy you can recover, the
only thing that is going to save you money is to
actually use the energy in your facility, and by do- ACID FORMATION A LIMITING FACTOR
ing so, decrease the amount of outside energy you IN WASTE HEAT RECOVERY
have to purchase.
Typical uses for waste heat energy are: One of the most important factors influenc-
ing stack gas heat recovery is the corrosion prob-
a. Boiler feedwater heating lem accompanying the cooling of the gas. Because
b. Makeup water heating the sulfuric acid dew point is higher than the wa-
c. Combustion air preheating ter vapor dew point, heat recovery efforts must
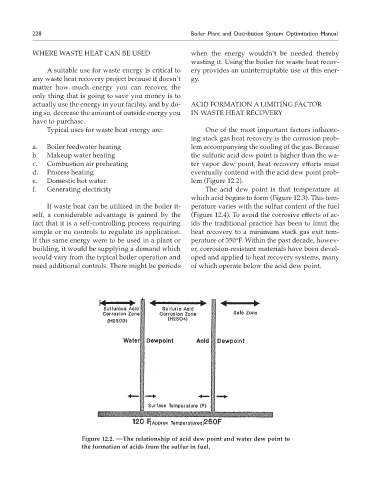
d. Process heating eventually contend with the acid dew point prob-
e. Domestic hot water lem (Figure 12.2).
f. Generating electricity The acid dew point is that temperature at
which acid begins to form (Figure 12.3). This tem-
If waste heat can be utilized in the boiler it- perature varies with the sulfur content of the fuel
self, a considerable advantage is gained by the (Figure 12.4). To avoid the corrosive effects of ac-
fact that it is a self-controlling process requiring ids the traditional practice has been to limit the
simple or no controls to regulate its application. heat recovery to a minimum stack gas exit tem-
If this same energy were to be used in a plant or perature of 350°F. Within the past decade, howev-
building, it would be supplying a demand which er, corrosion-resistant materials have been devel-
would vary from the typical boiler operation and oped and applied to heat recovery systems, many
need additional controls. There might be periods of which operate below the acid dew point.
Figure 12.2. —The relationship of acid dew point and water dew point to
the formation of acids from the sulfur in fuel.